Table of Contents
Symptoms of Blood Clots in Urine: Key Indicators
Blood in urine, medically known as hematuria, can manifest in various forms, and recognizing the symptoms is critical for diagnosis and treatment. The presence of blood clots in urine often accompanies other symptoms that indicate potential health concerns.
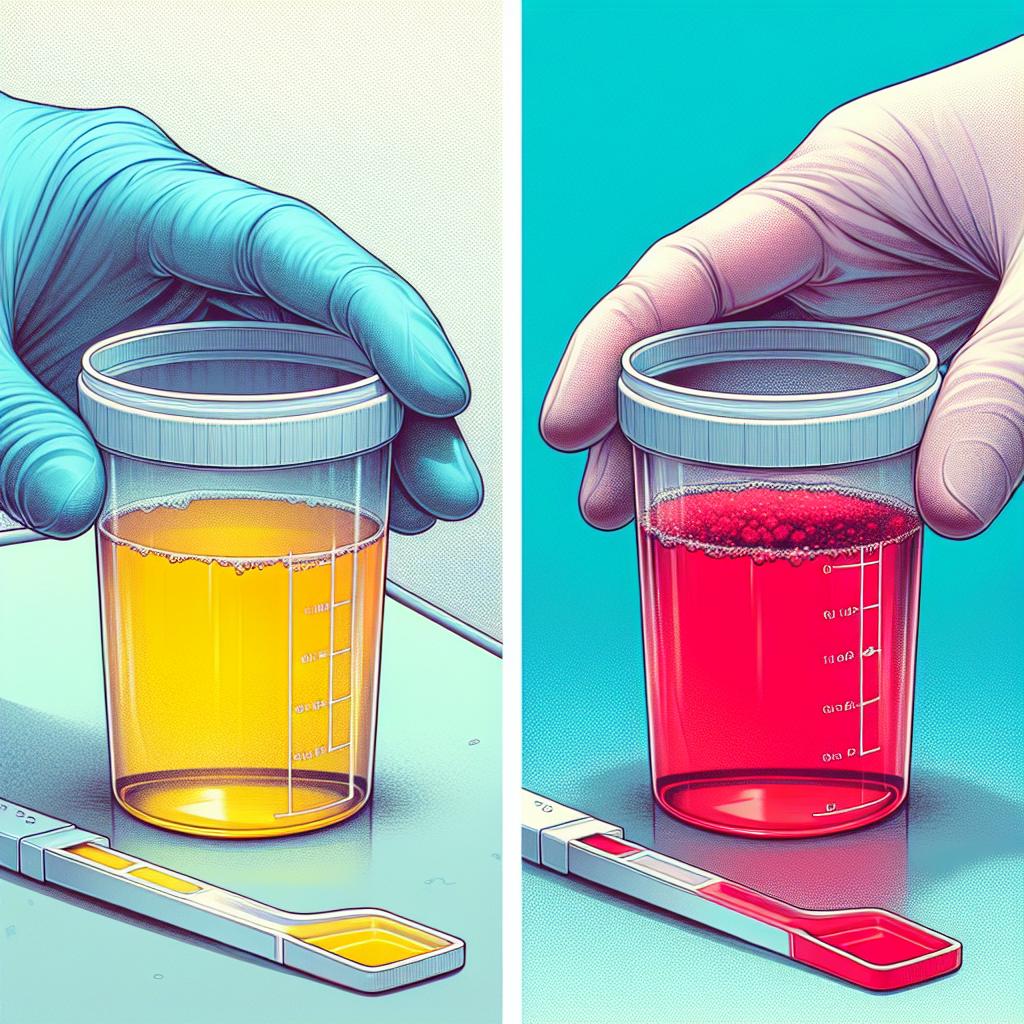
One of the most noticeable symptoms is the change in urine color. Individuals may observe pink, red, or brown urine, which can be indicative of blood presence. The size and frequency of blood clots can vary, with some appearing as small specks and others as larger masses. Moreover, patients might also experience pain during urination, known as dysuria, which can signal inflammation or irritation in the urinary tract (Cohen, 2023).
Additional symptoms may include frequent urination, an urgent need to urinate, and lower abdominal pain or discomfort. These signs can be indicative of infections, kidney stones, or other urinary tract issues. It is essential to pay attention to these symptoms, as they can provide valuable information for healthcare providers in diagnosing the underlying cause of blood clots in urine.
Visual Characteristics: Identifying Blood Clots in Urine
Identifying the visual characteristics of blood clots in urine is essential for understanding the severity of the condition. Blood clots can vary in appearance, and their characteristics can provide insights into the potential causes.
Typically, blood clots in urine appear as dark red or brown specks, but they can also present as larger clumps. The consistency of these clots may range from jelly-like to solid, and they can be accompanied by other particles or sediment in the urine. The presence of blood clots can also lead to turbidity, giving the urine a cloudy appearance. This cloudiness may suggest the presence of additional substances, such as pus or mucus, which could indicate an infection (Johnson, 2023).
When assessing the visual characteristics, it is crucial to consider the context in which the blood clots appear. For instance, if blood clots are observed after strenuous physical activity or trauma, they may be related to injuries. Conversely, if they are consistently present without any apparent cause, it may indicate underlying medical conditions such as bladder or kidney stones, infections, or tumors.
Causes of Blood Clots in Urine: Understanding the Triggers
The causes of blood clots in urine can be diverse and may arise from various medical conditions. Understanding these triggers is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment.
One common cause of blood clots in urine is urinary tract infections (UTIs). UTIs can lead to inflammation and irritation of the urinary tract, resulting in bleeding and the formation of clots. Symptoms of UTIs often include a burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy urine (Smith, 2023).
Kidney stones are another prevalent cause of blood clots in urine. These hard deposits can form in the kidneys and travel through the urinary tract, causing pain and bleeding. The size of the kidney stones can vary, and larger stones may cause more significant damage, leading to heavier bleeding and larger clots (Brown, 2023).
Additionally, more severe conditions such as tumors in the bladder or kidneys can cause hematuria. These tumors may be benign or malignant, and their presence can lead to bleeding in the urinary tract. Other potential causes include trauma to the urinary system, certain medications that may increase bleeding risk, and blood disorders that affect clotting (Davis, 2023).
Understanding the underlying causes of blood clots in urine can help individuals identify when to seek medical attention and facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Blood in Urine
Recognizing when to seek medical attention for blood in urine is crucial for health management. If you notice blood clots in urine, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional, especially if accompanied by severe symptoms.
Immediate medical attention should be sought if there is a sudden onset of blood in urine with significant pain, fever, or chills. These symptoms may indicate a severe infection or other urgent medical conditions. Furthermore, if there is a history of kidney disease, cancer, or blood disorders, the presence of blood clots in urine should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider (Taylor, 2023).
Routine check-ups and examinations are also advisable, even if symptoms seem mild. Regular screenings can help identify potential issues early and prevent complications. Healthcare providers may conduct various tests, including urinalysis, blood tests, imaging studies, or cystoscopy, to determine the underlying cause of blood clots in urine (Miller, 2023).
Treatment Options for Blood Clots in Urine: What to Expect
The treatment options for blood clots in urine depend on the underlying cause. A thorough diagnosis is essential to tailor the treatment approach effectively.
For infections such as UTIs, antibiotics are typically prescribed to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Pain relief medications may also be recommended to alleviate discomfort during urination (Wilson, 2023).
In cases where kidney stones are the cause, treatment options may include increased fluid intake to help flush out smaller stones. Larger stones may require more invasive procedures, such as shock wave lithotripsy or surgical intervention to remove them (Evans, 2023).
If tumors or more serious conditions are detected, treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, depending on the nature and stage of the tumor. Blood disorders may require specific treatments to manage clotting issues and prevent further complications (Clark, 2023).
While the treatment plan will vary based on the diagnosis, it is essential to follow up with healthcare providers regularly to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary.
FAQ Section
What should I do if I see blood clots in my urine?
If you notice blood clots in your urine, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an evaluation, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as pain or fever.
Are blood clots in urine always a sign of a serious condition?
Not always, but they can indicate various health issues, from infections to kidney stones or tumors. A thorough examination is necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
Can dehydration cause blood clots in urine?
Dehydration can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, which may lead to blood clots in urine. Staying adequately hydrated is essential for urinary tract health.
How are blood clots in urine diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a urinalysis, imaging tests, and possibly cystoscopy to determine the underlying cause of blood clots in urine.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent blood clots in urine?
Maintaining proper hydration, practicing good hygiene, and managing underlying health conditions can help reduce the risk of blood clots in urine.
References
- Cohen, J. (2023). Signs of Blood in Urine: Understanding Hematuria
- Johnson, L. (2023). Urinary Tract Health: Visual Indicators of Medical Conditions
- Smith, A. (2023). The Impact of Urinary Tract Infections on Hematuria
- Brown, R. (2023). Kidney Stones: Formation, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Davis, K. (2023). Tumors and Hematuria: A Comprehensive Overview
- Taylor, M. (2023). When to Seek Medical Attention for Hematuria
- Miller, D. (2023). Diagnostic Approaches to Hematuria
- Wilson, T. (2023). Antibiotic Treatment for Urinary Tract Infections
- Evans, P. (2023). Treatment Options for Kidney Stones: A Review
- Clark, H. (2023). Managing Blood Disorders: Treatment and Prevention