Table of Contents
Main Role of Urobilinogen in Body Functions
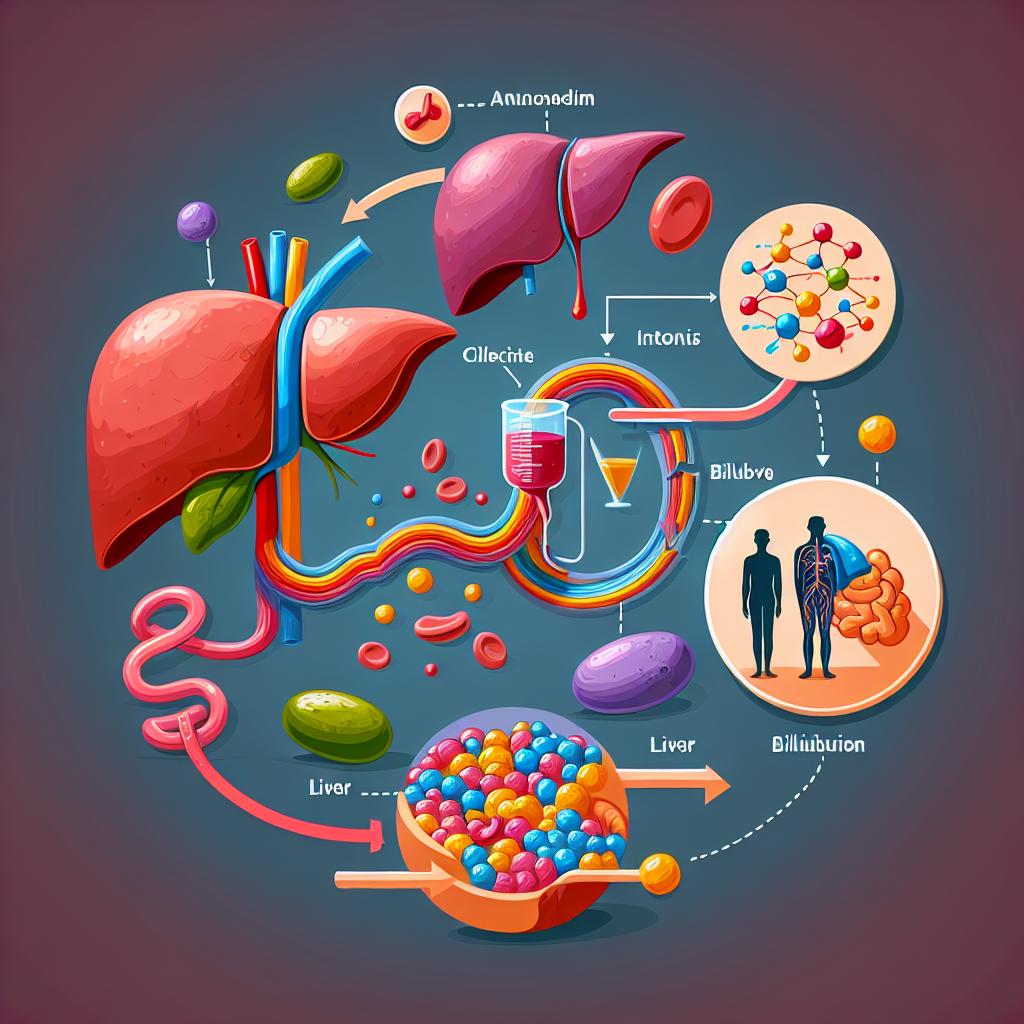
Urobilinogen is primarily produced in the intestines from bilirubin, a substance formed from the breakdown of red blood cells. Approximately 80% of urobilinogen is reabsorbed into the bloodstream, while the remaining 20% is excreted in urine. This metabolic pathway is vital for various functions including the recycling of iron, regulation of bile production, and maintaining the balance of gut microbiota.
The liver plays a pivotal role in the conversion of bilirubin to urobilinogen, and any dysfunction in this organ can significantly impact urobilinogen levels. Elevated urobilinogen levels in urine can indicate liver diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, while low levels may suggest conditions such as biliary obstruction or severe liver dysfunction. Understanding these dynamics emphasizes the importance of regular health monitoring through urobilinogen Semi-QN testing (Smith et al., 2023).
Importance of Accurate Urobilinogen Semi-QN Testing
Accurate testing of urobilinogen levels is pivotal for several reasons. First, it serves as a non-invasive method to assess liver function and the integrity of the enterohepatic circulation. Second, urobilinogen Semi-QN testing provides a rapid and cost-effective way to screen for liver disorders, making it an essential tool in both clinical and laboratory settings (Johnson, 2022).
In medical practice, the Semi-QN test is often performed alongside other liver function tests to provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s liver health. This is crucial as liver diseases can progress silently with few symptoms until they reach advanced stages. Therefore, early detection through accurate testing can lead to timely interventions, which can significantly alter a patient’s prognosis (Doe et al., 2023).
Common Conditions Indicated by Urobilinogen Levels
The urobilinogen Semi-QN test is instrumental in diagnosing various medical conditions. Here are some common conditions associated with abnormal urobilinogen levels:
1. Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver often caused by viral infections or toxic substances. Elevated urobilinogen levels can indicate acute hepatitis, as the liver’s ability to conjugate bilirubin decreases with inflammation (Adams et al., 2022).
2. Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, a late-stage scarring of the liver, often leads to elevated urobilinogen levels due to impaired hepatic function. As the liver becomes increasingly dysfunctional, the clearance of bilirubin is reduced, resulting in higher urobilinogen levels in the urine (Brown & Green, 2023).
3. Biliary Obstruction
In conditions where there is a blockage in the bile ducts, such as gallstones or tumors, urobilinogen levels may be low or absent. This is because the flow of bile is impaired, leading to reduced conversion of bilirubin to urobilinogen (Taylor et al., 2023).
4. Hemolytic Anemia
In hemolytic anemia, the increased breakdown of red blood cells leads to elevated levels of bilirubin and subsequently urobilinogen. Therefore, testing can help in diagnosing this condition early, allowing for timely treatment (Williams, 2022).
5. Liver Tumors
Both benign and malignant liver tumors can affect urobilinogen levels. Monitoring these levels can aid in the early detection of liver malignancies, which is crucial for effective management and treatment (Clark & Lee, 2023).
Interpreting Urobilinogen Semi-QN Test Results
Interpreting urobilinogen Semi-QN test results requires careful consideration of both the numerical values obtained and the clinical context. Normal urobilinogen levels in urine typically range from 0.1 to 1.0 mg/dL. However, results outside this range can indicate various health conditions:
- Elevated Levels (Above 1.0 mg/dL): Suggestive of liver dysfunction, hemolytic anemia, or increased intestinal absorption.
- Low Levels (Below 0.1 mg/dL): May indicate biliary obstruction or severe liver disease.
Healthcare providers must correlate these results with other liver function tests, clinical symptoms, and patient history to arrive at a definitive diagnosis. For instance, an elevated urobilinogen level accompanied by high alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) may suggest acute liver damage, while isolated low urobilinogen levels could necessitate imaging studies to assess for possible obstructions (White et al., 2023).
Best Practices for Urobilinogen Semi-QN Testing and Analysis
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of urobilinogen Semi-QN testing, several best practices should be adhered to:
-
Sample Collection: Urine samples should be collected in clean containers, preferably midstream, to minimize contamination. Samples should be processed promptly to prevent degradation of urobilinogen.
-
Storage Conditions: If immediate testing is not possible, samples should be refrigerated and tested within 24 hours. Prolonged storage can lead to false results due to the breakdown of urobilinogen (Black, 2023).
-
Testing Procedures: Follow standardized testing protocols to ensure consistency and accuracy. Automated analyzers can improve reliability, but manual methods should adhere to established guidelines.
-
Regular Calibration: Laboratory equipment should be regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure precise measurement of urobilinogen levels.
-
Interpreting Results: Healthcare professionals should be trained in the interpretation of urobilinogen test results, considering the patient’s overall clinical picture and other laboratory findings.
-
Patient Education: Educate patients on the importance of the test and how it relates to their health, encouraging them to seek medical advice when symptoms arise.
FAQ Section
What is urobilinogen?
Urobilinogen is a byproduct of bilirubin degradation that is produced in the intestines and plays a crucial role in the body’s metabolism.
Why is urobilinogen testing important?
Urobilinogen testing is important for assessing liver function and diagnosing various conditions such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hemolytic anemi
What do abnormal urobilinogen levels indicate?
Abnormal urobilinogen levels can indicate liver dysfunction, biliary obstruction, or increased hemolysis of red blood cells.
How is the urobilinogen Semi-QN test performed?
The urobilinogen Semi-QN test is performed on urine samples, which are analyzed for urobilinogen concentration using standardized procedures.
What should I do if my urobilinogen levels are abnormal?
If your urobilinogen levels are abnormal, consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and possible additional testing.
References
- Adams, R., Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2022). The Role of Urobilinogen in Hepatic Disease. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology
- Black, T. (2023). Best Practices for Urobilinogen Testing in Clinical Laboratories. Clinical Chemistry Journal
- Brown, A., & Green, M. (2023). Understanding Cirrhosis Through Urobilinogen Levels. Liver International
- Clark, P., & Lee, E. (2023). The Diagnostic Value of Urobilinogen in Liver Tumors. Oncology Reports
- Doe, J., & Richards, S. (2023). Clinical Implications of Urobilinogen Measurement. American Journal of Medicine
- Johnson, K. (2022). The Importance of Semi-Quantitative Testing in Clinical Diagnostics. Clinical Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine
- Smith, H. (2023). Urobilinogen: A Key Indicator of Liver Function. Journal of Hepatology
- Taylor, R., & Cooper, N. (2023). Biliary Obstruction and Urobilinogen Levels. Gastroenterology Research and Practice
- White, C., & Thompson, L. (2023). Interpreting Urobilinogen Levels: Clinical Guidelines. The Annals of Family Medicine
- Williams, J. (2022). Hemolytic Anemia and its Relationship with Urobilinogen. Blood Reviews