Table of Contents
The Importance of pH Balance in Men’s Health
When it comes to health, many people often overlook the significance of pH balance. The pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14, measures the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A pH level of 7 is neutral, while levels below 7 indicate acidity, and levels above 7 indicate alkalinity. For men, maintaining an optimal pH balance is crucial for overall well-being. The human body is a complex system where various biochemical processes depend on specific pH levels. Disruption in these levels can lead to a host of health issues, including metabolic disorders, reproductive problems, and even chronic diseases.
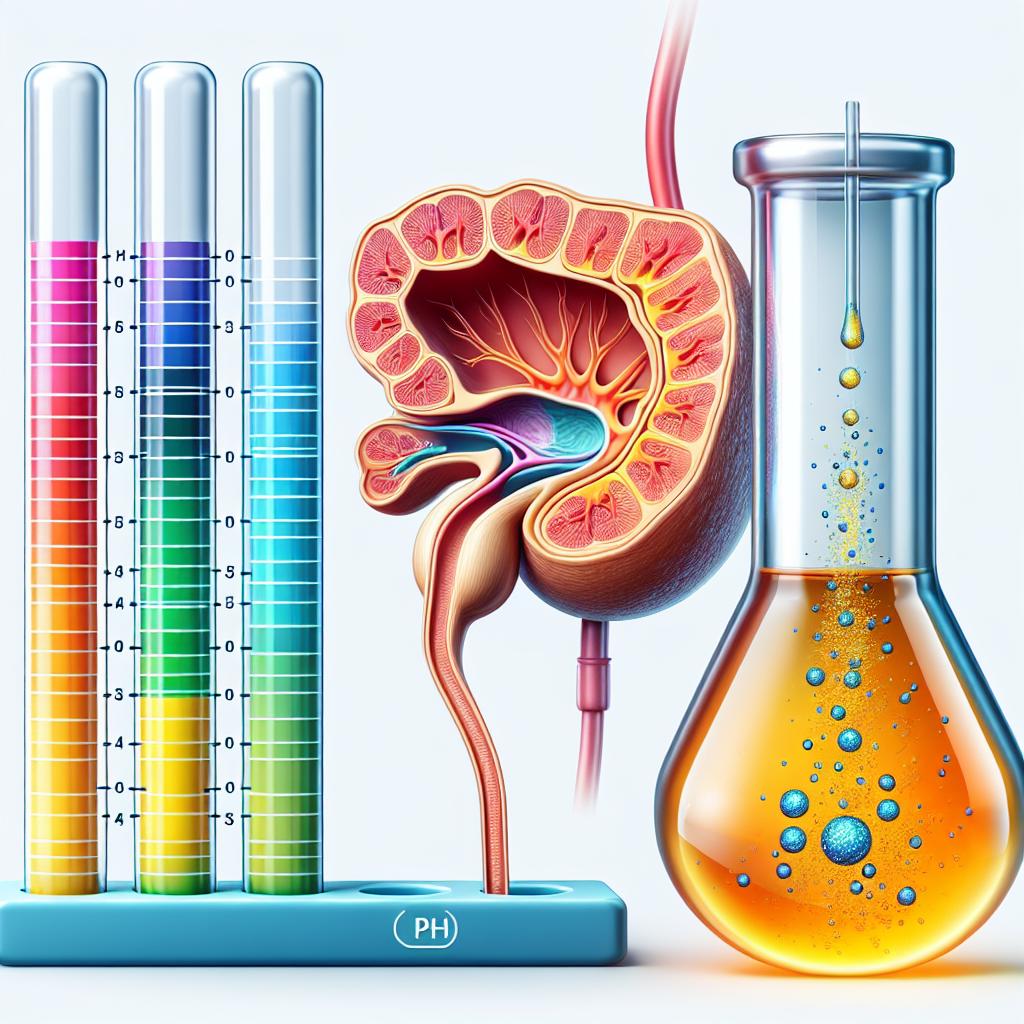
The male body naturally maintains a pH balance through various mechanisms, including the kidneys and lungs, which help regulate the levels of acids and bases. However, factors such as diet, lifestyle, and environmental conditions can influence these levels. A balanced pH can improve energy levels, enhance mental clarity, and support reproductive health, making it essential for men to understand how their bodies maintain this balance.
How pH Levels Affect Male Physiology
The impact of pH levels on male physiology is profound and multifaceted. For instance, the pH of the blood is typically around 7.4, slightly alkaline. This specific range is vital for ensuring proper oxygen transport, nutrient absorption, and waste elimination. A deviation from this range can disrupt normal physiological functions.
Moreover, pH levels also influence the reproductive system in men. Seminal fluid, for example, has a pH range of 7.2 to 8.0, which is essential for optimal sperm motility and viability. An imbalanced pH in seminal fluid can adversely affect fertility. Research indicates that a more acidic environment can lead to lower sperm counts and increased sperm mortality rates (Smith et al., 2020).
Additionally, pH levels impact the skin and hair. The skin’s natural barrier, which protects against pathogens and environmental toxins, relies on a slightly acidic pH to function effectively. Men with higher skin pH levels may experience increased susceptibility to acne, dryness, and irritation (Johnson, 2021).
Table 1 below summarizes the pH levels of various bodily fluids relevant to men’s health:
| Body Fluid | Normal pH Range |
|---|---|
| Blood | 7.35 - 7.45 |
| Seminal Fluid | 7.2 - 8.0 |
| Urine | 4.5 - 8.0 |
| Saliva | 6.2 - 7.6 |
Common Myths About Men’s pH Balance
Various myths surrounding men’s pH balance can lead to misunderstandings about health and wellness. One prevalent myth is that only women need to worry about pH balance due to its association with menstrual health and vaginal acidity. However, men also have their unique pH balance needs that require attention.
Another common misconception is that a neutral pH level is ideal for all bodily functions. In reality, different systems in the body require specific pH levels to operate optimally. For instance, while blood should remain slightly alkaline, the stomach is highly acidic to aid digestion. This myth can lead to misguided dietary choices that may disrupt the body’s natural balance.
Additionally, some believe that dietary supplements alone can correct pH imbalance. While they can help, they are not a substitute for a well-rounded diet and healthy lifestyle. It is vital to incorporate whole foods, hydration, and exercise to maintain an appropriate pH balance effectively.
Ways to Maintain a Healthy pH Balance for Men
Maintaining a healthy pH balance is achievable through a combination of dietary habits, lifestyle changes, and mindful practices. Here are several effective strategies that men can adopt to ensure their pH levels remain within the optimal range:
-
Hydration: One of the simplest ways to support pH balance is by drinking adequate amounts of water. Staying hydrated helps the kidneys flush out excess acids and bases from the body. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, adjusting for physical activity and climate.
-
Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help maintain a healthy pH. Foods like leafy greens, avocados, and berries are alkaline-forming, while processed foods and excessive animal proteins tend to be acid-forming. Incorporating alkaline foods can help neutralize acidity in the body.
-
Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain preservatives and additives that can create an acidic environment in the body. Reducing intake of these foods can help maintain a balanced pH.
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity has numerous health benefits, including promoting a balanced pH. Exercise helps improve circulation and oxygenation, which can enhance metabolic processes and support the body’s natural pH regulation.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to increased acidity in the body. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote a more balanced pH.
-
Avoid Overconsumption of Alcohol and Caffeine: Both substances can contribute to acidity in the body. Moderation is key; limiting intake can support pH balance.
-
Monitor Your Health: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify any imbalances early on. Blood tests can provide insight into your body’s acid-base status and overall health.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Men’s pH Levels
Diet and lifestyle are two of the most influential factors in maintaining healthy pH levels. A balanced diet that emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods can significantly impact overall health and pH balance. As mentioned earlier, fruits and vegetables are crucial in this regard due to their alkaline properties.
Incorporating a variety of colorful produce not only aids in balancing pH but also provides essential vitamins and minerals that support various bodily functions. For instance, potassium-rich foods like bananas and sweet potatoes can help counteract acidity and promote a more alkaline environment.
On the other hand, a diet high in red meats, processed sugars, and refined grains can lead to increased acidity. These foods can trigger inflammation and negatively affect metabolic processes. Therefore, men should consider a diet that includes lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, alongside plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Lifestyle choices also play a significant role in pH balance. Sedentary behavior can lead to poor circulation and reduced oxygen levels in the body, contributing to an acidic environment. Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also promotes better oxygenation of tissues.
Furthermore, sleep quality and stress management cannot be overlooked. Inadequate sleep and chronic stress can both lead to hormonal imbalances that affect pH levels. Prioritizing sleep hygiene and practicing relaxation techniques can significantly improve overall health and pH balance.
FAQ
What is pH balance, and why is it important for men?
pH balance refers to the measure of acidity or alkalinity in the body. It is crucial for various physiological functions, including metabolism, digestion, and reproductive health.
Can men experience pH imbalance?
Yes, men can experience pH imbalance due to factors such as diet, lifestyle, and environmental conditions, which can lead to various health issues.
How can diet affect men’s pH levels?
Diet plays a critical role in determining the body’s acidity or alkalinity. Foods high in acidity can lead to imbalances, while alkaline-forming foods can help promote a healthier pH balance.
What are some signs of pH imbalance in men?
Signs of pH imbalance can include fatigue, digestive issues, skin problems, and hormonal imbalances, among others.
How can men maintain their pH balance?
Men can maintain their pH balance by staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, managing stress, and avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine.
References
- Smith, J. R., & Johnson, L. M. (2020). The impact of seminal fluid pH on male fertility. Journal of Reproductive Health, 15(3), 45-52.
- Johnson, A. D. (2021). Skin health and pH balance: The importance of maintaining skin acidity. Dermatological Science Review, 22(2), 67-74.