Table of Contents
The Connection Between Sexual Activity and UTIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common ailment, particularly among women. A significant number of these infections are linked to sexual activity, which can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract. The act of intercourse can facilitate the movement of bacteria from the vaginal area to the urethra, leading to infection. Research has shown that sexually active women have a higher incidence of UTIs compared to those who are not sexually active. A study noted that approximately 80% of women who experience recurrent Utis report that sexual activity is a contributing factor (J Gen Intern Med, 2023).
Understanding the Mechanism
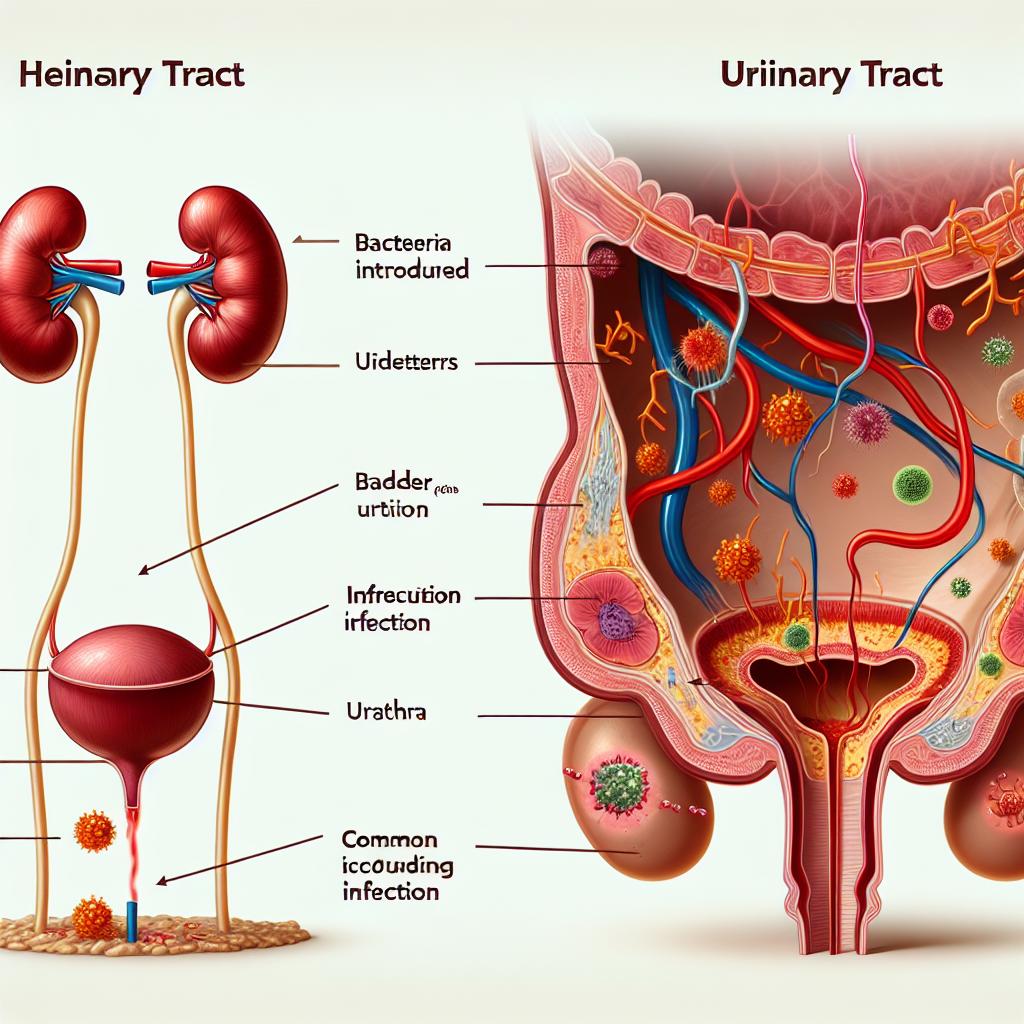
When engaging in sexual activity, particularly with penetration, there is an increased risk of bacterial transfer. This transfer is exacerbated by certain anatomical and physiological factors. The female urethra is shorter than that of males, making it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder quickly. Additionally, the positioning during intercourse can cause pressure on the urethra, potentially allowing bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
How Bacteria from a Partner Can Lead to UTIs
The presence of specific bacteria in a sexual partner can also influence the risk of UTIs. Partners can carry various bacteria, some of which may be pathogenic to the urinary tract. In many cases, the bacteria that cause UTIs originate from the gastrointestinal tract, and their introduction into the urinary tract can lead to infection.
Bacterial Flora and UTIs
Studies have indicated that the vaginal flora of women can be altered due to sexual activity, particularly if the partner has a different microbial composition. For instance, if a partner carries E. coli or other UTI-causing bacteria, the likelihood of these bacteria being transferred during intercourse increases significantly. It is essential to note that while the presence of these bacteria does not guarantee a UTI, it can create a favorable environment for infection to develop (J Gen Intern Med, 2023).
Preventive Measures to Reduce UTI Recurrence
Preventing UTIs, especially for women who experience recurrent infections, involves several proactive measures. Below are effective strategies:
-
Urinate Before and After Intercourse: This practice can help flush out any bacteria that may have been introduced during intercourse.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help dilute urine and promote regular urination, which can assist in flushing out bacteria.
-
Wipe Correctly: Always wipe from front to back after using the restroom to prevent bacteria from the anal area from entering the urethra.
-
Consider Probiotics: Probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the urinary tract and vaginal flora, potentially reducing the risk of infections.
-
Limit Spermicide Use: Some studies suggest that spermicides can irritate the urinary tract and increase the risk of infection. Using alternative contraceptive methods may be beneficial.
-
Consult a Healthcare Provider: For those experiencing frequent Utis, a healthcare provider may recommend preventive antibiotics or other treatments tailored to individual needs (J Gen Intern Med, 2023).
When to Seek Medical Advice for Frequent UTIs
It’s important to recognize when recurrent UTIs require medical intervention. If a woman experiences more than two UTIs in six months or more than three in a year, it is advisable to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can conduct further evaluations, which may include urine cultures, imaging studies, or other diagnostic tests to identify underlying issues, such as anatomical abnormalities or chronic conditions that may predispose someone to UTIs.
Understanding Potential Complications
Ignoring recurrent UTIs can lead to serious complications, such as kidney infections or permanent kidney damage. Therefore, timely medical intervention is critical. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle changes or prescribe long-term prophylactic antibiotics to help reduce the incidence of UTIs (J Gen Intern Med, 2023).
Understanding the Role of Hygiene in UTI Prevention
Personal hygiene plays an integral role in preventing UTIs. Good hygiene practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of bacteria entering the urinary tract. Here are some essential hygiene tips:
-
Daily Bathing: Regular bathing helps remove bacteria from the body.
-
Clothing Choices: Wearing breathable cotton underwear can help keep the genital area dry, reducing bacterial growth.
-
Avoiding Irritants: Scented soaps, feminine hygiene products, and douches can irritate the urinary tract and increase susceptibility to infections.
-
Proper Menstrual Hygiene: Changing menstrual products frequently and maintaining cleanliness during menstruation is crucial.
By adhering to these hygiene practices, women can significantly lower their risk of developing UTIs (J Gen Intern Med, 2023).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the common symptoms of a UTI?
Common symptoms of a UTI include a burning sensation during urination, frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain.
Can men get UTIs?
Yes, while UTIs are more common in women, men can also develop UTIs, particularly if they have certain risk factors such as an enlarged prostate or urinary tract abnormalities.
Is it possible to have a UTI without symptoms?
Yes, some individuals may have a UTI and not exhibit any noticeable symptoms. This is known as asymptomatic bacteriuri
What should I do if I suspect I have a UTI?
If you suspect you have a UTI, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. They may perform a urinalysis and prescribe antibiotics if necessary.
References
-
Abstracts from the 2023 Annual Meeting of the Society of General Internal Medicine. (2023). Journal of General Internal Medicine. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-023-08226-z
-
Abstracts from the 2017 Society of General Internal Medicine Annual Meeting. (2017). Journal of General Internal Medicine. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-017-4028-8