Table of Contents
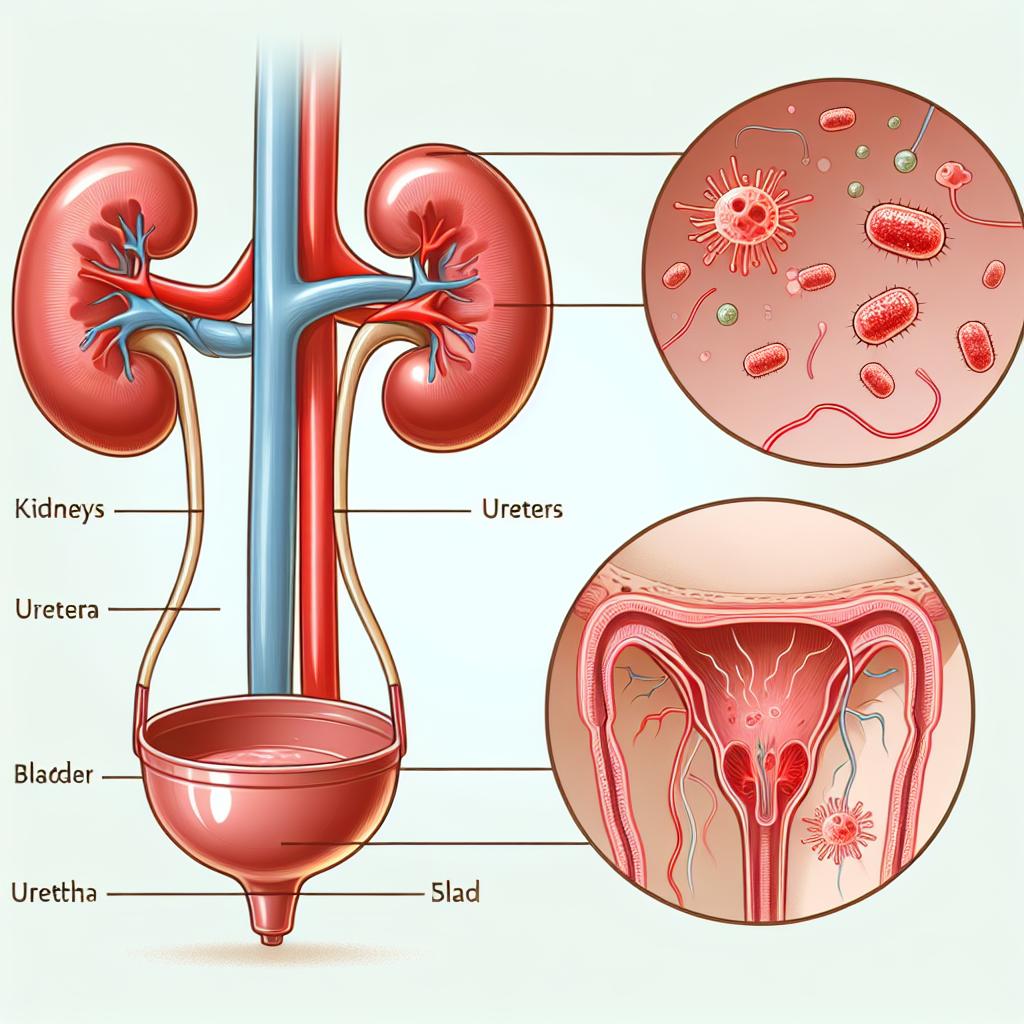
Common Causes of Mucus in Urine for Women
Several factors can contribute to the presence of mucus in urine. Understanding these causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Here are some common causes:
-
Normal Physiological Response: Mucus is produced naturally in the urinary tract as a protective mechanism. It helps to trap pathogens and debris, preventing infections. Therefore, a small amount of mucus can be considered normal.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): UTIs are one of the leading causes of mucus in urine. When bacteria infect the urinary tract, the body responds by producing more mucus to combat the infection. Symptoms may include frequent urination, burning sensation during urination, and cloudy urine.
-
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Certain STIs, such as gonorrhea and chlamydia, can lead to increased mucus production in urine. These infections often present with additional symptoms, including unusual discharge, pelvic pain, and discomfort during intercourse.
-
Vaginal Infections: Conditions like bacterial vaginosis or yeast infections can result in mucus in urine, particularly if there is an associated discharge. Women may experience itching, irritation, or abnormal vaginal discharge alongside mucus in urine.
-
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle can lead to variations in mucus production. For instance, during ovulation, women often experience increased cervical mucus, which may sometimes mix with urine.
-
Dehydration: Insufficient hydration can cause urine to become concentrated, leading to the thickening of mucus. Adequate fluid intake is essential for maintaining healthy urine composition.
-
Kidney Stones: The presence of kidney stones can lead to inflammation and irritation in the urinary tract, resulting in increased mucus production. Symptoms may include severe pain, blood in urine, and frequent urination.
-
Chronic Conditions: Certain chronic diseases, such as diabetes or interstitial cystitis, may cause mucus to appear in urine due to ongoing irritation or infection in the urinary tract.
Symptoms Accompanying Mucus in Female Urine
The presence of mucus in urine may be accompanied by various symptoms, depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate, often associated with UTIs or bladder infections.
- Burning Sensation: A painful or burning feeling during urination can indicate an infection.
- Cloudy Urine: Mucus may cause urine to appear cloudy or turbid, especially in cases of infection.
- Abnormal Discharge: Unusual vaginal discharge may accompany mucus in urine, particularly in cases of STIs or vaginal infections.
- Pelvic Pain: Women may experience pelvic or abdominal discomfort, especially if the mucus is related to an infection or inflammation.
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for seeking timely medical attention and preventing complications.
Diagnosis of Mucus Presence in Women’s Urine
Diagnosing the cause of mucus in urine typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Here’s how healthcare professionals approach this diagnosis:
-
Medical History: Patients will be asked about their symptoms, duration, and any potential exposure to infections or irritants. This includes discussing any recent sexual activity, hygiene practices, and history of urinary tract or vaginal infections.
-
Physical Examination: A thorough examination may be conducted to assess any physical signs of infection or inflammation. This may include a pelvic examination for women.
-
Urinalysis: A urinalysis is essential for evaluating urine composition. This test checks for the presence of red and white blood cells, bacteria, and other substances. The presence of high levels of mucus, along with other indicators, can help narrow down potential causes.
-
Culture Tests: If a urinary tract infection or STI is suspected, urine cultures may be performed to identify the specific bacteria or virus causing the infection.
-
Imaging Studies: In certain cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans may be recommended to check for kidney stones or other abnormalities in the urinary tract.
-
Vaginal Swabs: In cases where a vaginal infection is suspected, swabs may be taken to identify the presence of pathogens.
Effective Treatments and Management for Mucus in Urine
Treatment for mucus in urine largely depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common management strategies:
-
Antibiotics: If a urinary tract infection or sexually transmitted infection is diagnosed, antibiotics will likely be prescribed to eliminate the infection.
-
Hydration: Increasing fluid intake helps dilute urine and may reduce mucus concentration. This approach is especially useful for mild cases or dehydration-related mucus.
-
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications can help alleviate discomfort associated with infections or inflammation.
-
Hormonal Management: If hormonal fluctuations are the cause of increased mucus, healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle changes or hormonal therapies to regulate hormone levels.
-
Probiotics: For women experiencing recurrent infections or imbalances in vaginal flora, probiotics may help restore normal bacterial levels and prevent future infections.
-
Surgical Interventions: In cases involving kidney stones or significant anatomical abnormalities, surgical procedures may be necessary to correct the underlying issue.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Good personal hygiene, safe sexual practices, and regular medical check-ups can help prevent infections and maintain overall urinary health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is mucus in urine always a cause for concern?
Not necessarily. A small amount of mucus in urine can be normal. However, if accompanied by other symptoms like pain or unusual discharge, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
How can I reduce mucus in my urine?
Staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and treating any underlying infections can help manage mucus levels in urine. Consult with a doctor for tailored advice.
Can hormonal changes cause mucus in urine?
Yes, hormonal fluctuations, particularly during the menstrual cycle, can increase mucus production. This is often normal and not a cause for concern.
What tests are done to diagnose mucus in urine?
A urinalysis, culture tests, and, in some cases, imaging studies or vaginal swabs may be performed to identify the cause of mucus in urine.
When should I see a doctor for mucus in urine?
If you experience significant changes in urine appearance, such as increased mucus, pain during urination, or unusual discharge, it’s important to seek medical attention.
References
-
Castellanos-Ruiz, D., Ojeda-Borbolla, J. G., Ruiz-García, O. V., Peña-Corona, S. I., Martínez-Peña, A. A., Ibarra-Rubio, M. E., Gavilanes-Ruiz, M., Mendoza-Rodríguez, C. A., & Gagné, F. (2025). Uterine Microbiota and Bisphenols: Novel Influencers in Reproductive Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15010026
-
Mazzinelli, E., Favuzzi, I., & Nocca, G. (2025). Development of an Innovative Dual Construct for Targeted Drug Delivery in the Oral Cavity. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17020272
-
Jonas, L. C., Youngs, C. R., & Schmitz-Esser, S. (2025). Combined analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequencing data reveals core vaginal bacteria across livestock species. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1524000
-
Ansari, P., Reberio, A. D., Ansari, N. J., Kumar, S., Khan, J. T., Chowdhury, S., Abd El-Mordy, F. M., & Hannan, J. M. A. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of Medicinal Plants and Their Phytoconstituents in Diabetes, Cancer, Infections, Cardiovascular Diseases, Inflammation and Gastrointestinal Disorders. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020454
-
Impact of Smoking on Cervical Histopathological Changes in High-Risk HPV-Positive Women: A Matched Case–Control Study. (2025). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020235
-
A case of infantile reversible cytochrome C oxidase deficiency myopathy in Taiwan: A 4-year follow-up. (2025). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11858699/