Table of Contents
What is UTI and What Causes Instant Relief Needs?
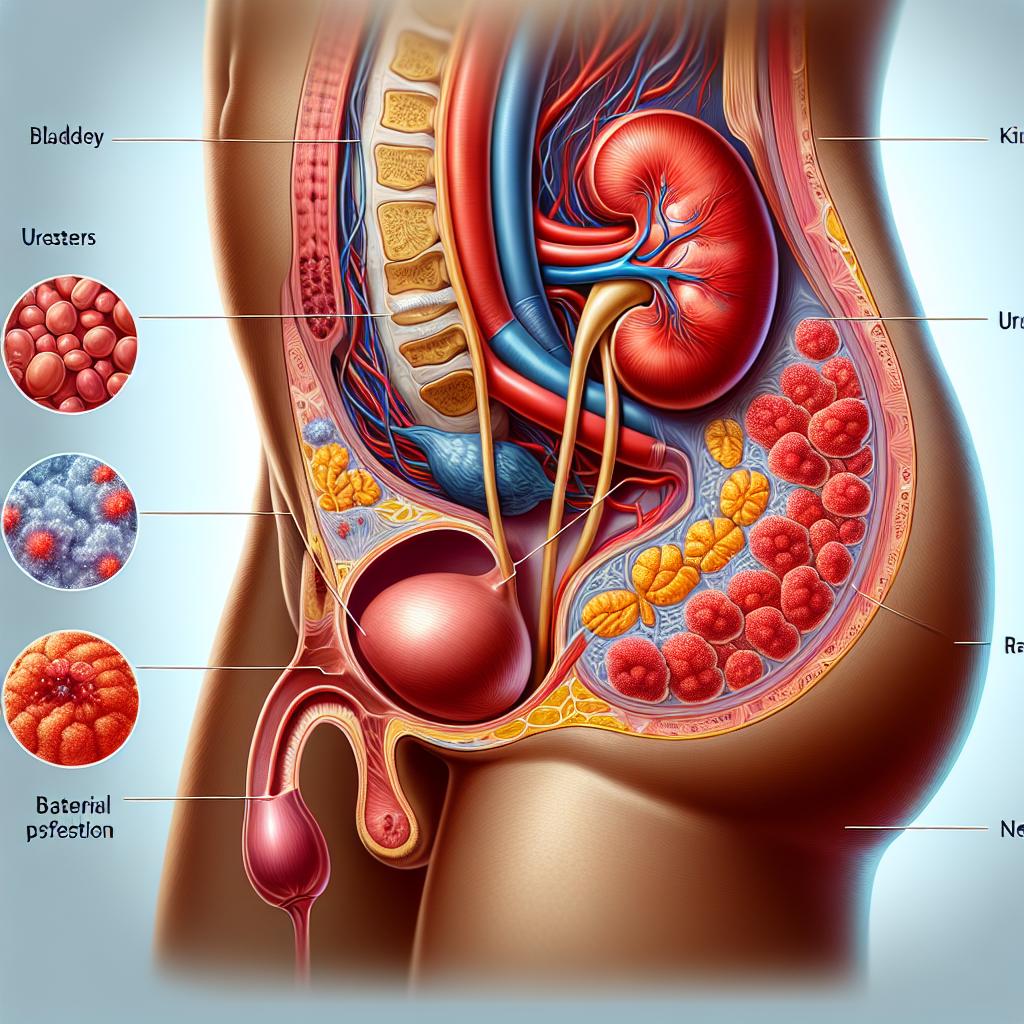
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common infections that affect the urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. UTIs occur when bacteria, often from the gastrointestinal tract, enter the urinary tract and multiply. The most common bacteria involved in UTIs are Escherichia coli (E. coli), accounting for approximately 80% of cases. Other bacteria may also cause UTIs, though less frequently. Factors contributing to the need for instant relief include anatomical differences, sexual activity, certain contraceptive methods, and underlying health conditions such as diabetes or a weakened immune system (1).
A UTI can manifest quickly, necessitating immediate relief solutions, particularly for individuals who experience recurrent infections. Symptoms may start mildly but can escalate, leading to discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. The urgency for effective and quick solutions is paramount for individuals who find themselves in acute discomfort, thus requiring both an understanding of the infection and accessible relief measures (2).
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Instant UTI Relief
Recognizing UTI symptoms is crucial for prompt treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination: A strong, persistent urge to urinate, often producing only small amounts of urine.
- Burning sensation: Pain or discomfort during urination, commonly referred to as dysuria.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine: Changes in urine appearance or odor can indicate infection.
- Pelvic pain: Discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
- Blood in urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can also be a warning sign.
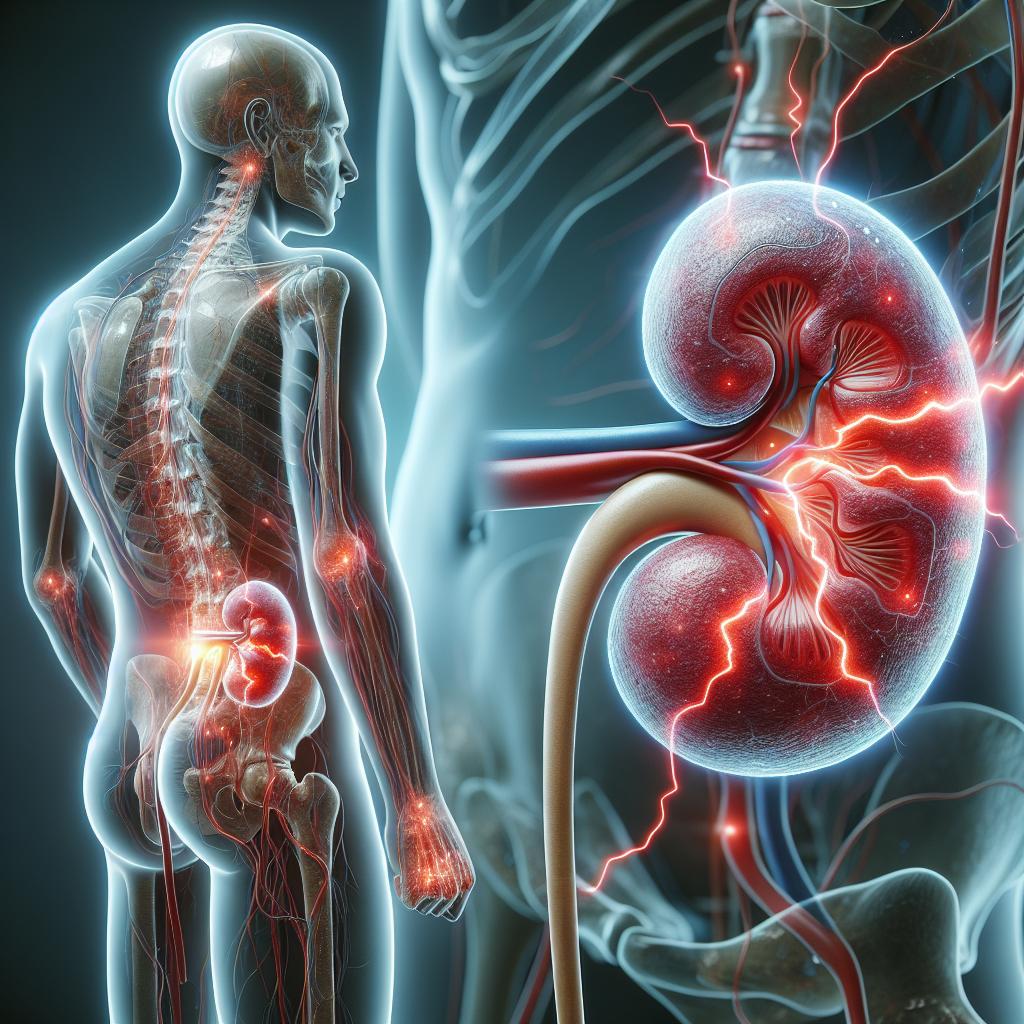
In severe cases, UTIs may lead to more systemic symptoms, such as fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting, indicating a possible kidney infection, which requires immediate medical intervention. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek relief promptly to avoid complications (3).
Home Remedies for Instant UTI Relief
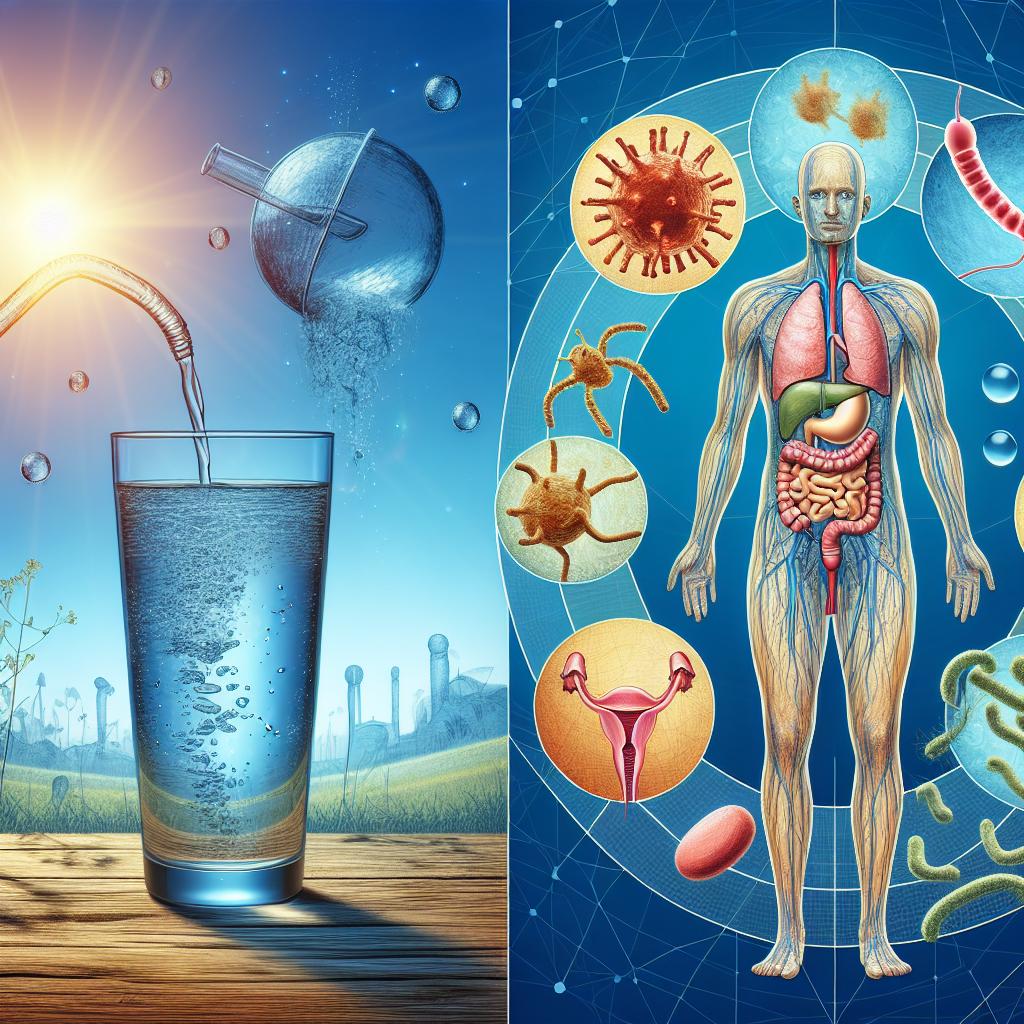
Many individuals seek immediate relief from UTIs through home remedies before consulting healthcare providers. Some effective home remedies include:
-
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush out bacteria from the urinary tract, speeding up recovery.
-
Cranberry Juice: Cranberries contain compounds that may prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall, potentially reducing UTI recurrence. Unsweetened cranberry juice is recommended for optimal benefits (4).
-
Baking Soda: Mixing a teaspoon of baking soda in water may help neutralize acidity in the urine, providing relief from burning sensations during urination. However, this should be consumed cautiously and not regularly as it can affect pH balance.
-
Probiotics: Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt can help restore the natural flora of the urinary tract, potentially preventing further infections.
-
Heating Pad: Applying a heating pad to the lower abdomen can alleviate discomfort and pain associated with UTIs.
-
D-Mannose: This simple sugar can help prevent certain bacteria from sticking to urinary tract walls. It is available as a supplement and may offer relief for some individuals.
-
Garlic: Known for its antibacterial properties, consuming garlic can help combat the bacteria causing the infection (5).
While these remedies may help with discomfort and may prevent recurrence, they should not replace professional medical advice, especially in severe cases.
Over-the-Counter Solutions for Quick UTI Relief
In addition to home remedies, several over-the-counter (OTC) solutions can provide quick relief from UTI symptoms:
-
Phenazopyridine: This medication provides relief from pain, burning, urgency, and frequency associated with UTIs. It works as a urinary analgesic, providing symptomatic relief rather than treating the infection itself. It is typically used for short durations (6).
-
Urinary Antiseptics: Some OTC products contain ingredients to help cleanse the urinary tract, though they do not replace antibiotics for treating an active infection.
-
Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and discomfort.
-
Hydration Tablets: These may assist in restoring electrolyte balance while promoting adequate hydration.
-
Herbal Supplements: Products containing ingredients like uva ursi may provide mild relief, but their efficacy is debated (7).
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication or supplement, especially if symptoms persist.
When to Seek Professional Help for UTI Relief
While home remedies and OTC medications can provide relief, it is essential to know when to seek professional help. Consider contacting a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms persist for more than 24 hours despite home treatment.
- You experience severe abdominal or pelvic pain.
- There is blood in your urine.
- You develop a fever above 101°F (38.3°C).
- You have symptoms of a kidney infection, such as back pain, chills, or vomiting (8).
Healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics to treat the underlying infection effectively. A urine culture may also be conducted to determine the specific bacteria causing the infection and to tailor treatment effectively.
Conclusion
UTIs are a common and uncomfortable condition that can escalate quickly, making instant relief essential for those affected. Understanding the symptoms, utilizing home remedies, and knowing when to seek professional help can significantly improve outcomes and comfort levels. While OTC solutions can provide temporary relief, consulting with a healthcare provider remains the best approach for addressing the root cause and ensuring proper treatment.
FAQ
What is a UTI?
A UTI, or urinary tract infection, is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethr
How can I prevent UTIs?
To prevent UTIs, practice good hygiene, drink plenty of water, urinate after intercourse, avoid irritating feminine products, and consider wearing breathable cotton underwear.
Can I treat a UTI at home?
Mild UTIs can sometimes be treated at home with increased fluid intake, cranberry juice, and OTC medications. However, persistent or severe symptoms require medical attention.
When should I see a doctor for a UTI?
If your symptoms persist for more than 24 hours, worsen, or if you experience severe pain, fever, or blood in your urine, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
Are there any long-term effects of UTIs?
Recurrent Utis can lead to complications, such as kidney infections or permanent kidney damage. It is essential to properly manage and treat UTIs to prevent such outcomes.
References
-
Gaulton, A., Bellis, L. J., Bento, A. P., Chambers, J., Davies, M., & Ochoa, M. (2017). ChEMBL: A large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Research, 45(D1), D945-D954
-
Ashburn, T. T., & Thor, K. B. (2004). Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 3(8), 673-683. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1468
-
Matta, A., O’Neill, H. M., & Al-Juburi, J. (2020). Potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs identified by a drug repurposing strategy. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 85, 107221
-
Khamis, M. M., & Kadi, A. A. (2021). Drug repurposing for COVID-19: A systematic review. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 653329
-
Zeng, Z., Lin, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., & Li, H. (2020). Drug repositioning for COVID-19: A systematic review. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11, 588. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00588
-
FDA. (2020). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA issues emergency use authorization for potential COVID-19 treatment
-
Kirtman, B. P., & Min, D. (2021). Predicting the future of the COVID-19 pandemic: How the science of forecasting works. Nature, 593, 153-154
-
Hooton, T. M. (2012). Urinary tract infection: Diagnosis and management. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America, 26(4), 855-878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2012.08.001