Table of Contents
Importance of Early Detection of UTIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections, especially in women. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications such as kidney infections, recurrent UTIs, and chronic health issues. The importance of early detection cannot be overstated, as untreated UTIs can lead to severe health outcomes, including renal damage and systemic infections.
According to recent studies, the incidence of UTIs in women can be as high as 50% at least once in their lifetime, with recurrent infections affecting many of these individuals (Achan et al., 2025). Early detection through effective diagnostic methods can significantly reduce the morbidity associated with UTIs, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Moreover, the rise of antibiotic resistance has made it even more critical to accurately diagnose UTIs and initiate appropriate treatment early. The rapid evolution of antibiotic-resistant strains poses a challenge to healthcare systems globally, necessitating effective screening and management strategies (Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators, 2022).
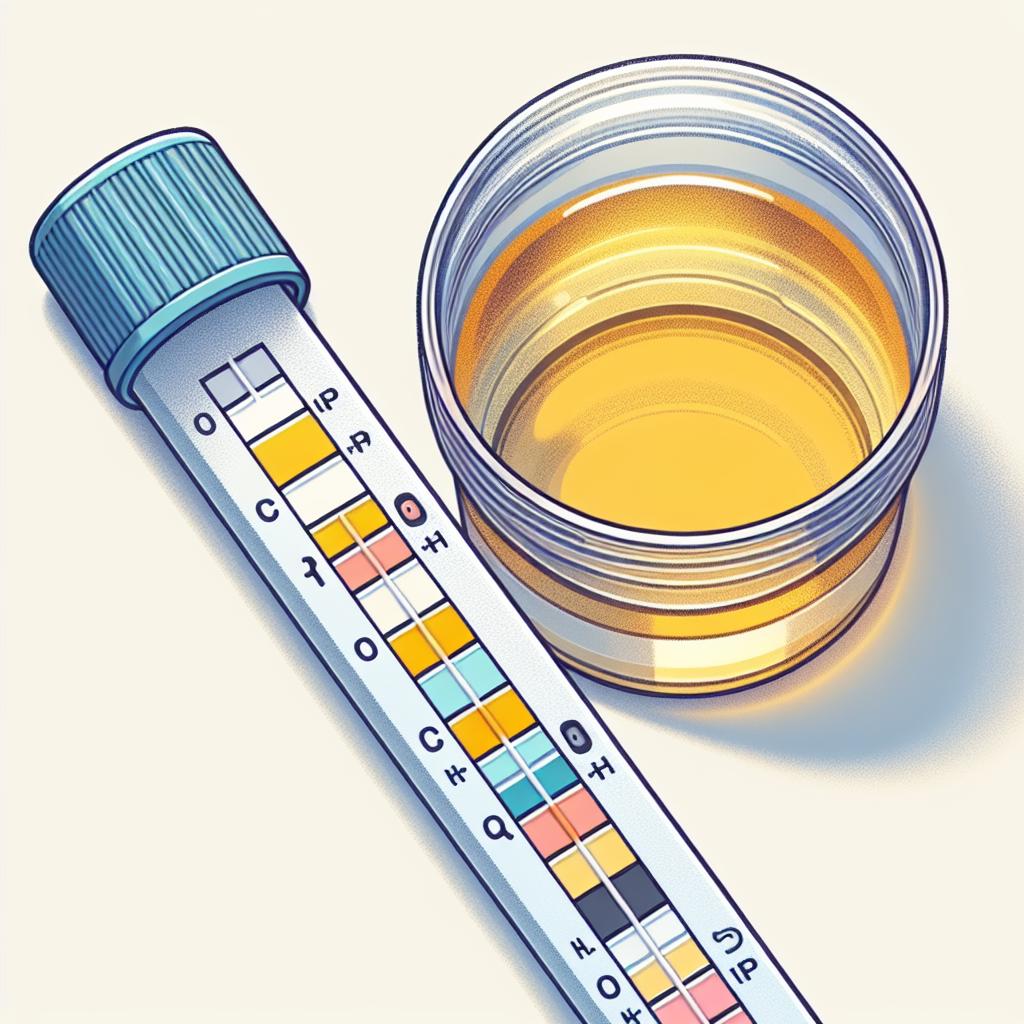
Overview of Over the Counter UTI Tests
Over the counter (OTC) UTI tests have become increasingly popular due to their accessibility and convenience. These tests typically include dipstick tests that can detect the presence of nitrites and leukocyte esterase in urine, both indicators of a urinary tract infection.
Types of OTC UTI Tests
-
Dipstick Tests: These are the most common OTC products. They are easy to use and provide rapid results. Users dip a test strip into a urine sample and compare the color change to a chart provided with the test kit.
-
Urine Culture Kits: Some advanced kits allow users to collect urine samples that can be sent to labs for culture and sensitivity testing, although these are less common than dipstick tests.
-
Combination Tests: Some products combine multiple tests for a more comprehensive assessment, checking for multiple markers associated with UTIs.
The convenience of these tests enables individuals to self-screen for UTIs, which can expedite treatment. However, it is essential to follow up with a healthcare professional for confirmation and further management, as false positives and negatives can occur.
How Over the Counter UTI Tests Work
OTC UTI tests primarily function by detecting specific substances that are present in urine during an infection. The two most critical indicators are:
-
Nitrites: Certain bacteria that cause UTIs convert urinary nitrates to nitrites. A positive result suggests the presence of these bacteria.
-
Leukocyte Esterase: This enzyme is released by white blood cells in response to infection. The presence of leukocyte esterase indicates inflammation and infection in the urinary tract.
Testing Procedure
The testing procedure is straightforward:
-
Collect a Urine Sample: The first morning urine is often recommended for the most accurate results.
-
Dip the Test Strip: Immerse the test strip in the urine sample for the specified time.
-
Wait for Color Change: After a set time, compare the color on the strip to the provided chart to determine the presence of nitrites and leukocyte esterase.
-
Interpret Results: A positive result for either marker suggests a possible UTI, prompting further consultation with a healthcare provider.
Limitations of OTC Tests
While OTC tests offer convenience, they are not without limitations:
-
False Positives/Negatives: Certain medications, foods, or other conditions can affect test accuracy. For example, some antibiotics may produce false negatives.
-
No Specificity: OTC tests cannot identify the specific bacteria causing the infection or their antibiotic sensitivities.
-
Need for Confirmation: Positive results should always be confirmed with laboratory testing, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
Comparing Over the Counter UTI Tests with Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests remain the gold standard for diagnosing UTIs. They offer a more comprehensive analysis compared to OTC tests.
| Feature | Over the Counter Tests | Laboratory Tests |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Instant (minutes) | Hours to days |
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Additional Information | None | Bacterial culture and sensitivity |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
| Follow-up Required | Yes | Yes |
Advantages of Laboratory Tests
-
Higher Accuracy: Laboratory tests, particularly urine cultures, provide definitive diagnoses and identify specific pathogens along with their antibiotic sensitivities (State of the Art of Antimicrobial and Diagnostic Stewardship in Pediatric Setting, 2024).
-
Comprehensive Data: They offer additional information such as the presence of bacteria, resistance patterns, and the exact pathogen involved.
-
Guided Treatment: Results from laboratory tests can help in tailoring antibiotic therapy, which is vital in the era of rising antibiotic resistance.
Tips for Using Over the Counter UTI Tests Effectively
-
Follow Instructions Carefully: Ensure you read and follow the instructions provided with the test kit for accurate results.
-
Timing Matters: Use the first morning urine for testing, as it tends to be more concentrated and provides reliable results.
-
Consult a Healthcare Provider: If the test indicates a UTI, seek medical advice for confirmation and appropriate treatment.
-
Monitor Symptoms: Keep track of any symptoms such as fever, chills, or flank pain, which could indicate more severe infection requiring immediate medical attention.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract and may assist in preventing infections.
FAQ
How accurate are OTC UTI tests?
OTC UTI tests are moderately accurate but can produce false positives or negatives. They are best used as a preliminary screening tool, not a definitive diagnosis.
What should I do if my OTC test is positive?
Consult a healthcare provider for further testing and to discuss treatment options.
Can I rely solely on OTC tests for UTI diagnosis?
No, while they can indicate the likelihood of a UTI, laboratory tests are necessary for confirmation and to identify the specific bacteria involved.
How often should I test for UTIs?
If you have recurrent UTIs or symptoms, discuss with your healthcare provider about a testing schedule that is right for you.
Are there any risks associated with not treating a UTI?
Yes, untreated UTIs can lead to more serious complications, including kidney infections, sepsis, and increased risk of recurrent infections.
References
-
Achan, B., Luggya, T., Ebwongu, R. I., Sekyanzi, S., & Kajumbula, H. (2025). Tossing the coin of extended-spectrum β-lactamase: prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from patients with sepsis. Access Microbiology, 25(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1099/acmi.0.000962.v3
-
Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet, 399(10325), 629–655 21)02653-2
-
State of the Art of Antimicrobial and Diagnostic Stewardship in Pediatric Setting. (2024). Antibiotics, 14(2), 132-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14020132