Table of Contents
Common Causes of Frequent Urinary Tract Infections
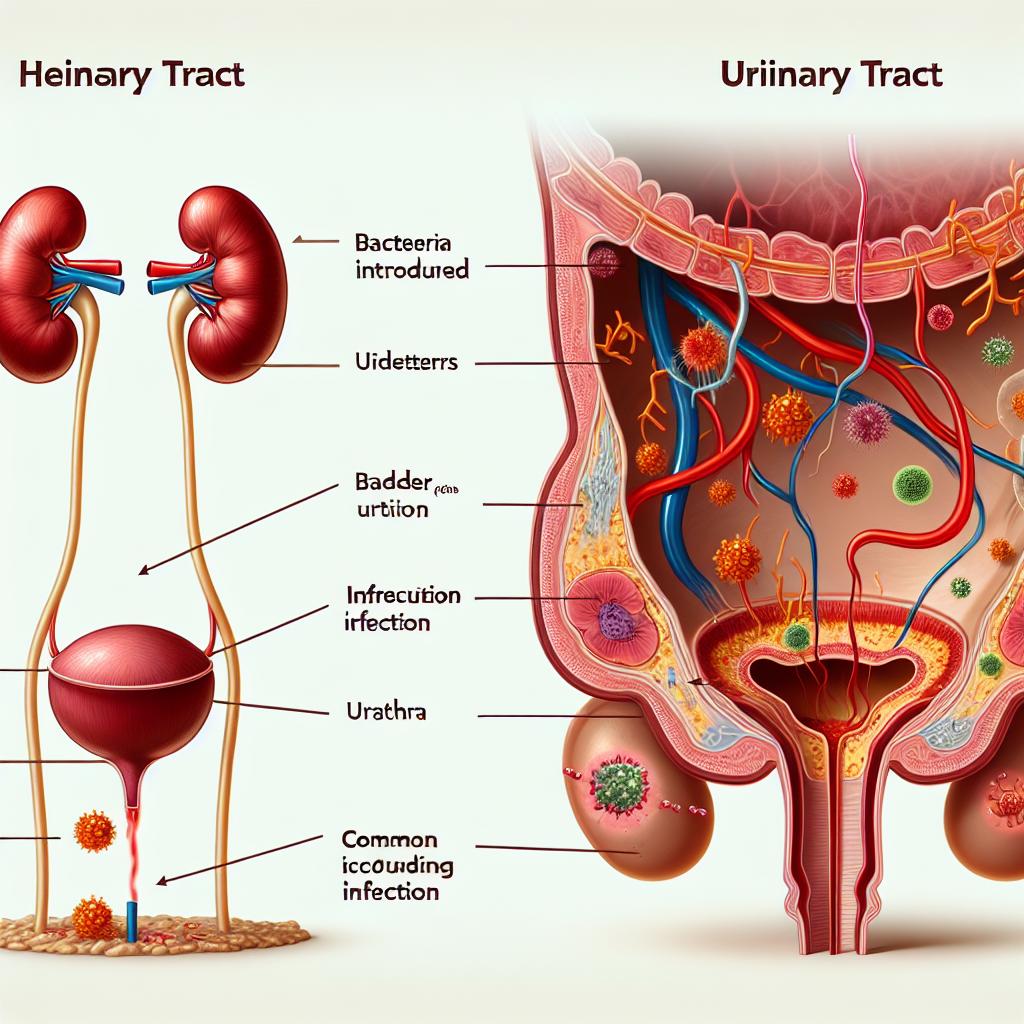
Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health concern, particularly among women. Understanding the underlying causes of these recurrent infections is crucial for effective prevention and management. The urinary tract comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and infections can occur in any of these areas. The primary cause of UTIs is the invasion of bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), into the urinary tract. This bacterium is typically found in the intestines but can easily enter the urinary tract through the urethra.
Several factors contribute to the likelihood of developing a UTI. One significant cause is improper hygiene practices. For example, wiping from back to front after using the toilet can transfer bacteria from the anus to the urethra, increasing the risk of infection. Additionally, the use of certain contraceptives, such as spermicides and diaphragms, can alter the natural flora of the vagina and make it more susceptible to infections.
Hormonal changes, especially during menopause, can also contribute to the frequency of UTIs. Estrogen plays a vital role in maintaining the health of the vaginal and urinary tract flora. A decrease in estrogen levels can lead to a change in the vaginal environment, making it more favorable for harmful bacteria to thrive. Furthermore, urinary retention due to anatomical abnormalities or certain medical conditions can exacerbate the problem, as stagnant urine can serve as a breeding ground for bacteria.
Risk Factors Contributing to Recurrent UTIs
In addition to the common causes mentioned above, there are several risk factors that significantly increase the likelihood of recurrent Utis. Understanding these risk factors is essential for individuals who suffer from frequent infections, as it can help guide preventive measures.
One of the most prominent risk factors is sexual activity. Women who are sexually active tend to have a higher incidence of UTIs, often referred to as “honeymoon cystitis.” The friction during intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra, leading to infection. Moreover, the use of certain birth control methods, such as diaphragms, can also increase the risk of UTIs due to their potential to irritate the urethra and alter the vaginal flora.
Another significant risk factor is urinary tract abnormalities. Structural issues, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate in men, can obstruct the flow of urine, making it easier for bacteria to proliferate and cause infections. Individuals with a history of UTIs are also at a higher risk; once a UTI occurs, there is an increased likelihood of subsequent infections.
Chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, can compromise the immune system, making it less effective at fighting off infections. Diabetics often experience changes in urine composition that can encourage bacterial growth. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems due to other conditions or medications are also at greater risk for frequent Utis.
Symptoms to Watch for in Urinary Tract Infections
Identifying the symptoms of a urinary tract infection is essential for prompt treatment and to prevent complications. The most common symptoms of UTIs include:
- Frequent Urge to Urinate: A person may feel the need to urinate more often than usual, even if little urine is produced.
- Burning Sensation: A burning sensation during urination is a hallmark symptom of a UTI and can be quite uncomfortable.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Urine may appear cloudy or have a strong odor, indicating the presence of bacteria.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the pelvic area or lower abdomen can accompany a UTI.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, may occur in some cases and is a serious symptom requiring immediate attention.
It is important to note that some individuals may experience mild symptoms or none at all, particularly in the elderly or those with weakened immune systems. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment, as untreated UTIs can lead to more severe complications, including kidney infections.
Effective Home Remedies for UTIs
While medical treatment is often necessary for managing urinary tract infections, several effective home remedies can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. These remedies focus on hydration, dietary adjustments, and natural antimicrobial properties.
-
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is fundamental in flushing out bacteria from the urinary tract. Increased fluid intake helps dilute urine and promotes frequent urination, which can help eliminate pathogens.
-
Cranberry Juice: Cranberry juice has long been touted as a home remedy for UTIs. It contains compounds called proanthocyanidins that can prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract walls. While cranberry juice may not cure a UTI, it can be a useful preventive measure.
-
D-Mannose: This simple sugar can also help prevent UTIs. D-mannose works similarly to cranberry by preventing bacteria from sticking to the urinary tract. It can be taken in powder form mixed with water.
-
Probiotics: Probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut and urinary tract. Consuming yogurt or supplements containing strains like Lactobacillus may reduce the risk of recurrent UTIs.
-
Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs, like uva ursi (bearberry) and garlic, possess natural antimicrobial properties. Uva ursi is known for its ability to soothe the urinary tract, while garlic can boost the immune response.
-
Adequate Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene can significantly reduce the risk of UTIs. This includes wiping from front to back, urinating after intercourse, and avoiding irritating feminine products.
While these home remedies can be beneficial, they should not replace professional medical advice or treatment, particularly for recurrent or severe infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention for UTIs
Understanding when to seek medical attention for urinary tract infections is vital for preventing complications. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional:
- Severe Pain: Intense pain in the lower abdomen or back that does not subside with over-the-counter pain relief may indicate a more severe infection.
- High Fever: A fever higher than 101°F (38.3°C) can be a sign of a kidney infection, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Persistent Symptoms: If UTI symptoms persist despite home treatment or over-the-counter medications, it is crucial to seek medical help.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can indicate a more serious infection, potentially affecting the kidneys.
- Recurrent UTIs: If you experience frequent UTIs, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and possible preventive measures.
Medical evaluation may include urine tests, imaging studies, or even a referral to a urologist if structural abnormalities are suspected. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from recurrent UTIs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the most common cause of urinary tract infections?
The most common cause of urinary tract infections is the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli), which typically originates from the gastrointestinal tract.
How can I prevent recurrent UTIs?
Preventive measures include practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, using cranberry products, and considering probiotics. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide additional strategies tailored to individual needs.
Are there any effective home remedies for UTIs?
Home remedies such as increased water intake, cranberry juice, D-mannose, probiotics, and certain herbal supplements can help alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
When should I see a doctor for a UTI?
You should seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, high fever, persistent symptoms, nausea, or recurrent UTIs. Early treatment is essential to prevent complications.
Can urinary tract infections lead to serious complications?
Yes, untreated UTIs can lead to serious complications, including kidney infections and sepsis, which can be life-threatening. Prompt treatment is crucial.
References
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2023). Urinary Tract Infection in Adults
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Hooton, T. M., & Scholes, D. (2022). Recurrent urinary tract infection in women. New England Journal of Medicine, 347(20), 1554-1557
- Foxman, B. (2022). The epidemiology of urinary tract infection. Nature Reviews Urology, 19(6), 389-395
- Gupta, K., & Hooton, T. M. (2023). Infections of the urinary tract. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America, 37(1), 1-18