Table of Contents
Introduction to UTIs and Sexual Activity
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that can affect individuals of all genders, but they are particularly prevalent among women. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, leading to inflammation and infection. The symptoms can be uncomfortable and distressing, often leading to questions regarding sexual activity during an active infection. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of UTIs, their symptoms, the risks associated with sexual activity while infected, and how to navigate intimacy during this time.
Understanding the implications of having sex with a UTI is critical for both physical and emotional health. Many individuals may feel confused about whether engaging in sexual activity is advisable, especially when experiencing the painful symptoms typical of a UTI. Therefore, it is essential to explore the nature of UTIs, the risks involved, and the best practices for maintaining sexual health during such infections.
Understanding UTIs: Causes and Symptoms
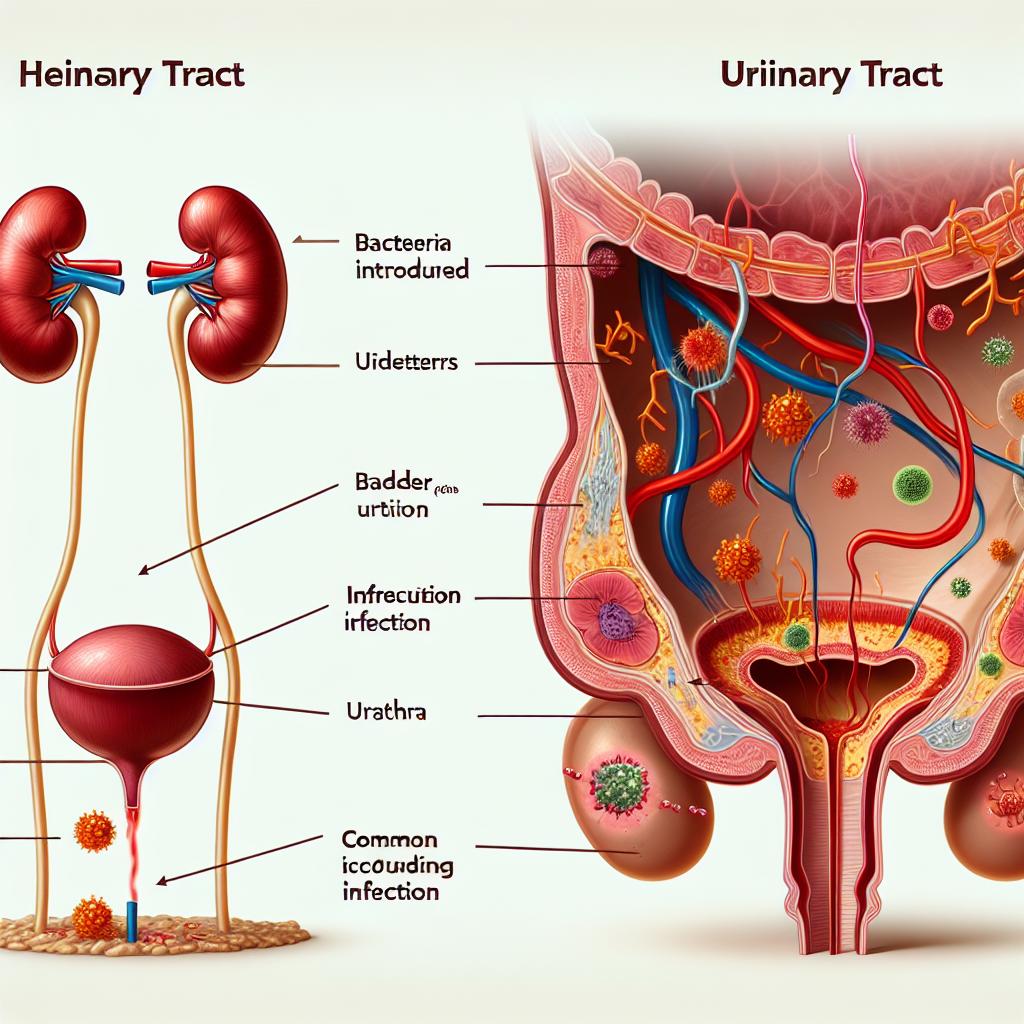
A UTI is usually caused by bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which are normally found in the intestines. These bacteria can enter the urinary system through the urethra and multiply in the bladder, leading to an infection. Factors that may increase the risk of developing a UTI include sexual activity, certain types of birth control, urinary tract abnormalities, and a weakened immune system.
Common Symptoms of a UTI
Symptoms of a UTI can vary but typically include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation while urinating
- Frequent urination of small amounts
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain or discomfort, particularly in women
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
These symptoms can cause significant discomfort and may affect one’s quality of life. Understanding these symptoms is crucial, as they can provide insight into when to seek medical attention.
Risks of Having Sex with a UTI
Engaging in sexual activity while suffering from a UTI can exacerbate symptoms and potentially lead to complications. The primary risks include:
-
Increased Discomfort: Sexual activity can heighten the discomfort associated with a UTI. The friction and pressure during intercourse may irritate the already inflamed tissues of the urinary tract, leading to increased pain and discomfort.
-
Potential for Complications: Having sex with a UTI may elevate the risk of developing a more severe infection, such as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). This is particularly a concern if the bacteria spread from the bladder to the kidneys.
-
Partner Transmission: While UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), certain bacteria can be transmitted to a partner during sexual activity. This can result in similar symptoms for the partner, leading to additional health issues.
-
Psychological Impact: The discomfort and potential embarrassment associated with having a UTI may also affect the emotional aspects of intimacy. This can lead to anxiety about sexual performance and overall sexual satisfaction.
Overall, the risks associated with having sex while experiencing a UTI often outweigh any potential benefits. It is generally advisable to avoid sexual activity until the infection has been treated and symptoms have resolved.
How to Manage Symptoms During Intimacy
If you find yourself in a situation where sexual activity is unavoidable, there are several strategies to manage UTI symptoms effectively. These practices aim to minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of complications.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is essential. Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract and may assist in alleviating some symptoms. Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily, or more if you are active.
Use of Lubricants
Using a water-based lubricant can help reduce friction during intercourse, minimizing discomfort. Avoid oil-based lubricants, as they can irritate the urinary tract further.
Gentle Approach
Engaging in gentle, non-invasive forms of intimacy can also be beneficial. Activities such as kissing, cuddling, and foreplay can foster intimacy without causing discomfort.
Communication with Your Partner
Being open and honest with your partner about your condition can help foster understanding and compassion. Discussing what feels comfortable and what may exacerbate symptoms can create a more supportive environment.
Safe Practices for Sex with a UTI
If you choose to engage in sexual activity while experiencing a UTI, implementing safe practices can help mitigate risks. Here are some essential guidelines:
-
Urinate Before and After Intercourse: This can help flush out any bacteria that may have been introduced during sexual activity.
-
Maintain Hygiene: Proper genital hygiene is crucial. Both partners should wash their hands and genitals before engaging in sexual activity to minimize the risk of introducing additional bacteria.
-
Avoid Certain Positions: Some sexual positions may cause more pressure on the bladder. Experimenting with positions that cause less discomfort can be beneficial.
-
Limit the Duration of Sexual Activity: Keeping sexual encounters shorter may help reduce irritation and discomfort associated with a UTI.
-
Consult a Healthcare Provider: If you have persistent symptoms or concerns about sexual activity during a UTI, consulting a healthcare professional is always advisable.
When to Seek Medical Advice for UTIs and Sexual Health
It is essential to seek medical advice if you experience any of the following:
- Symptoms of a UTI that persist for more than a day or two
- Fever or chills, which may indicate a more severe infection
- Blood in urine or severe abdominal pain
- A history of recurrent Utis
A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, ensuring that any underlying issues are addressed. Treatment often includes antibiotics to eliminate the infection and may involve lifestyle changes to prevent future occurrences.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help maintain urinary health. Discussing any concerns regarding sexual activity and urinary tract health can lead to improved outcomes and enhanced sexual well-being.
FAQ
Can having sex with a UTI make it worse?
Yes, engaging in sexual activity during a UTI can exacerbate symptoms and may lead to complications such as a kidney infection.
How long should I wait to have sex after a UTI?
It is advisable to wait until you are symptom-free and have completed your course of antibiotics before engaging in sexual activity.
Are there any safe sexual practices during a UTI?
Maintaining hygiene, using lubricants, and communicating with your partner about comfort levels can help make sexual activity safer during a UTI.
Can my partner get a UTI from me?
While UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections, certain bacteria can be transferred to a partner during sexual activity, potentially leading to similar symptoms.
What should I do if I experience recurrent UTIs?
Consulting a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and tailored prevention strategies is essential for managing recurrent UTIs.
References
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2021). Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) - Symptoms and Causes
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) - Diagnosis and Treatment
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2023). Urinary Tract Infections in Adults
- American Urological Association. (2023). Guidelines for the Management of UTI
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). UTI Symptoms and Treatment