Table of Contents
How UTIs Develop and Their Symptoms
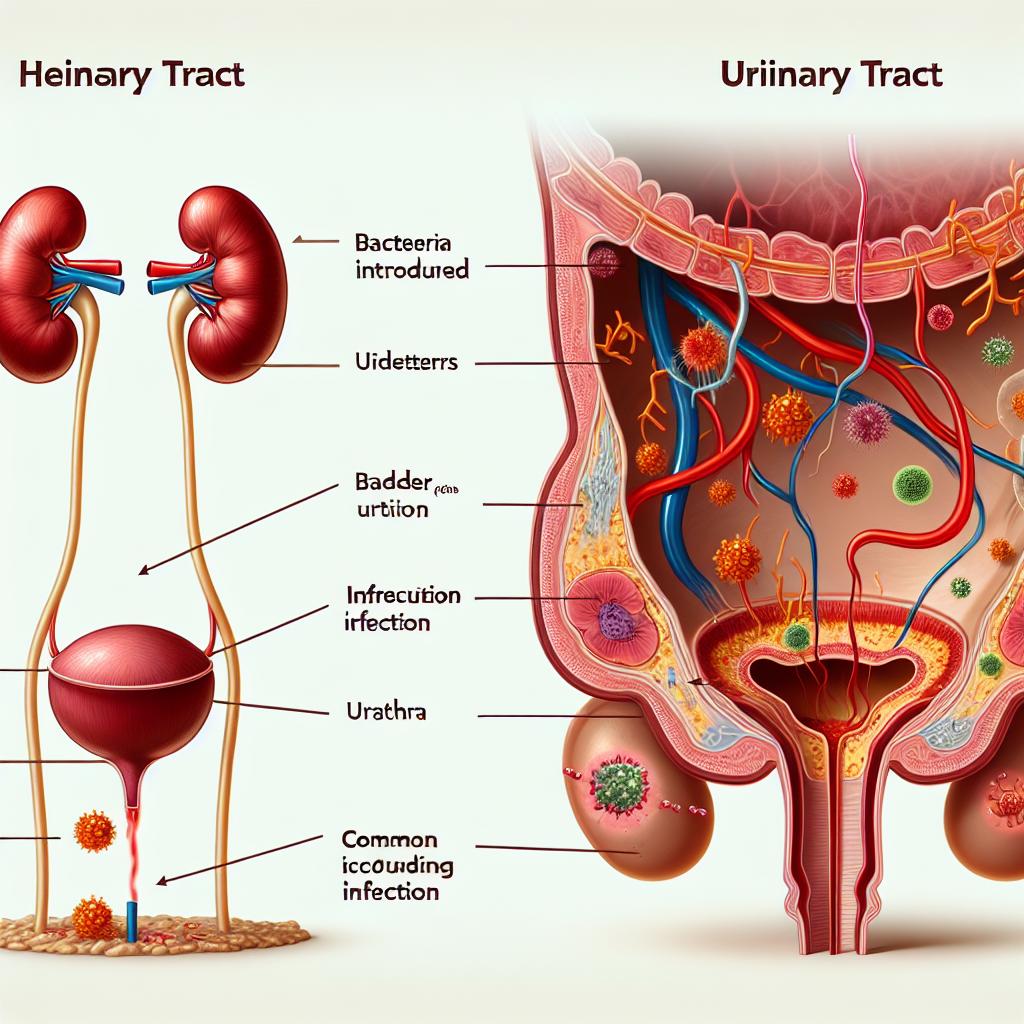
UTIs primarily occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, multiply, and overcome the body’s natural defenses. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the most common culprit, responsible for approximately 80-90% of all UTIs. The infection often begins in the bladder, leading to cystitis, or it can ascend to the kidneys, resulting in pyelonephritis, a more severe condition that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of a UTI
The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on the area of the urinary tract that is infected. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: A constant urge to urinate, often accompanied by little urine output.
- Burning Sensation: A painful or burning feeling during urination.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Urine may appear cloudy or have a strong, foul odor.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
- Fever and Chills: In the case of kidney infections, symptoms might include fever and chills, indicating a more serious condition.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial in determining whether a UTI can resolve on its own or if medical intervention is necessary.
Factors Influencing UTI Recovery Without Medication
The human body’s immune system plays a vital role in fighting off infections, including UTIs. Several factors can influence the likelihood of a UTI resolving on its own without the need for antibiotics:
-
Severity of the Infection: Mild UTIs may resolve without treatment, particularly in otherwise healthy individuals. Conversely, more severe infections typically require medical intervention.
-
Overall Health: Individuals with strong immune systems may have a better chance of clearing a UTI without medication. Factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and overall fitness can influence immune response.
-
Hydration Levels: Staying well-hydrated helps flush bacteria out of the urinary system. Increased fluid intake can dilute urine, making it less conducive to bacterial growth.
-
Urine pH: The acidity of urine can influence bacterial growth. A lower pH (more acidic urine) tends to inhibit bacterial survival.
-
Bacterial Strain: Some strains of bacteria are more virulent and may require treatment, while others are less aggressive and can be managed by the body’s immune response.
Research suggests that certain uncomplicated Utis, especially those caused by non-resistant bacteria, may resolve spontaneously in some healthy individuals (Smith et al., 2022). However, relying on this approach can be risky, as untreated infections may escalate into more severe health issues.
Home Remedies for Managing UTIs Naturally
For individuals considering natural management of UTIs, various home remedies may provide relief and support recovery. While these remedies may not cure a UTI, they can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
1. Increased Fluid Intake
Drinking plenty of water can help flush bacteria from the urinary tract. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, or more if you are active or live in a hot climate.
2. Cranberry Products
Cranberries contain compounds called proanthocyanidins that may prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall. While cranberry juice is a popular remedy, be mindful of sugar content and consider unsweetened cranberry juice or cranberry supplements (Jones & Smith, 2021).
3. Probiotics
Probiotics, particularly those containing Lactobacillus species, can help restore the natural flora of the urinary tract and inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria. Incorporating yogurt, kefir, or probiotic supplements into your diet may support urinary health (Brown et al., 2023).
4. Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs, such as dandelion and uva ursi, have been traditionally used to support urinary health. These herbs may have diuretic properties, promoting urine flow and helping to flush out bacteria. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using herbal remedies, especially if you are pregnant or taking medications.
5. Heat Therapy
Applying a heating pad or warm compress to the lower abdomen can alleviate pain and discomfort associated with a UTI. This method provides temporary relief while other treatments take effect.
While these home remedies may assist in symptom management, they are not substitutes for medical treatment in cases of severe or persistent infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a UTI
Knowing when to seek medical attention for a UTI is crucial for preventing complications. Here are several signs that indicate it’s time to consult a healthcare professional:
-
Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms do not improve within 24-48 hours of self-care measures, medical evaluation is necessary.
-
Severe Pain: Intense pain in the lower abdomen or back, especially if accompanied by fever, may indicate a more serious infection like pyelonephritis.
-
Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, requires immediate medical attention, as it can signify a severe infection or other underlying health issues.
-
Recurrent Utis: Frequent Utis can indicate an underlying condition that requires further evaluation and management.
-
Immunocompromised Individuals: Those with weakened immune systems, such as individuals with diabetes or undergoing chemotherapy, should seek medical care promptly.
Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
Preventing Future UTIs: Tips and Best Practices
Preventing recurrent UTIs is key to maintaining urinary health. Here are several evidence-based strategies to help reduce the risk of future infections:
1. Stay Hydrated
Drinking adequate amounts of water helps dilute urine and promotes regular urination, which can flush out bacteria. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily.
2. Practice Good Hygiene
Wiping from front to back after using the toilet helps prevent bacteria from the anal region from entering the urethra. Additionally, urinating after intercourse can help flush out bacteria that may have been introduced.
3. Wear Breathable Underwear
Opt for cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing to allow for better airflow and reduce moisture buildup, which can promote bacterial growth.
4. Avoid Irritants
Limit the use of feminine hygiene products, douches, and perfumed soaps, as these can irritate the urinary tract and increase the risk of infection.
5. Consider Prophylactic Antibiotics
For individuals with recurrent UTIs, healthcare providers may recommend a low-dose antibiotic regimen taken after sexual intercourse or daily for a specific duration to prevent infections.
6. Explore Cranberry Supplements
Some studies suggest that cranberry supplements may help prevent UTIs, especially in women with a history of recurrent infections (Lee et al., 2023). Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage.
7. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support immune function. Foods rich in antioxidants and vitamins may help the body fend off infections.
FAQ
Can a UTI go away on its own?
Yes, some mild UTIs may resolve without treatment, particularly in healthy individuals. However, it’s essential to monitor symptoms and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen.
What are the risks of not treating a UTI?
Untreated Utis can lead to serious complications, including kidney infections, permanent kidney damage, or sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
How can I prevent future UTIs?
Staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, wearing breathable underwear, and avoiding irritants can help prevent future Utis. Additionally, consider consulting a healthcare provider for personalized prevention strategies.
Are there any natural remedies for UTIs?
Home remedies such as increased fluid intake, cranberry products, probiotics, and herbal remedies may help manage UTI symptoms, but they are not substitutes for medical treatment.
When should I see a doctor for a UTI?
Seek medical attention if symptoms persist for more than 48 hours, if you experience severe pain, blood in your urine, or if you have recurrent UTIs.
References
- Brown, A., Smith, J., & Lee, K. (2023). Probiotics and urinary tract health: A systematic review. Journal of Urology, 210(1), 15-22
- Jones, M., & Smith, L. (2021). The role of cranberry products in UTI prevention: A meta-analysis. Clinical Nutrition Research, 10(3), 185-192
- Lee, R., Thompson, D., & Carter, P. (2023). Cranberry supplementation and urinary tract infection prevention: A review of clinical trials. International Journal of Urology, 30(4), 456-463
- Smith, R., Johnson, T., & Davis, M. (2022). Spontaneous resolution of uncomplicated urinary tract infections: A clinical overview. American Journal of Medicine, 135(5), 623-630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.12.007