Table of Contents
What is a UTI and How Does It Affect Your Body?
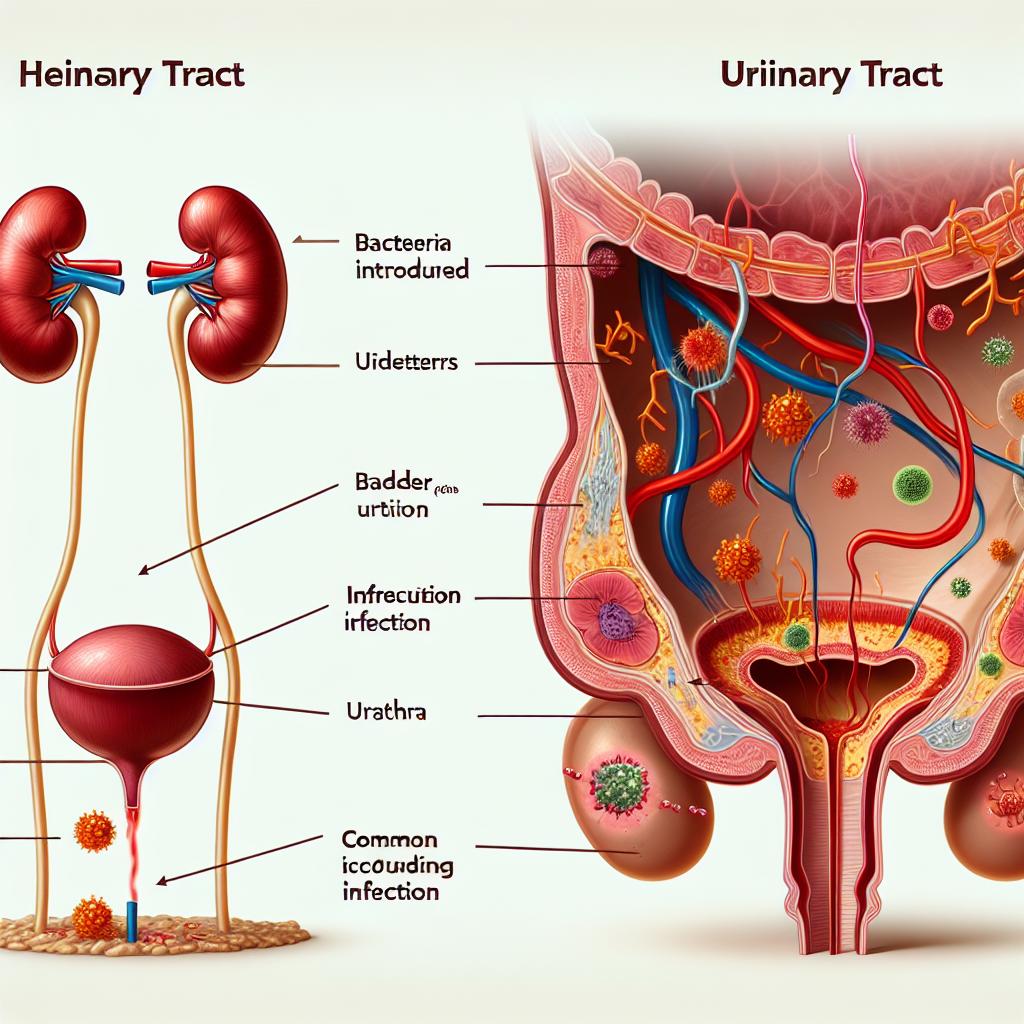
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that can occur in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most commonly, UTIs occur in the bladder and urethra. The infection is typically caused by bacteria, with Escherichia coli (E. coli) being the most prevalent culprit.
The presence of bacteria in the urinary tract triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the symptoms associated with UTIs. These infections are more common in women due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder. When a UTI develops, it can lead to various symptoms such as a burning sensation during urination, increased frequency of urination, and pelvic pain.
The body’s immune response to the infection can result in systemic effects as well, impacting overall wellbeing. This physiological response raises the question of whether such an infection can influence menstrual cycles and hormonal regulation.
Symptoms of a UTI: Recognizing the Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of a UTI is vital for timely treatment and to mitigate potential complications. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: A strong, persistent urge to urinate, even when the bladder may not be full.
- Burning Sensation: Pain or a burning feeling during urination is one of the hallmark signs of a UTI.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Urine may appear cloudy or have a strong odor.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area can also signify a UTI.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can occur and should be addressed immediately.
Early recognition of these symptoms can lead to prompt treatment, typically through antibiotics. Delaying treatment can allow the infection to worsen, potentially leading to more severe health issues, including kidney infections.
The Connection Between UTIs and Menstrual Irregularities
The relationship between UTIs and menstrual cycles is complex. While there is no direct evidence that a UTI can outright delay a period, the physiological stress caused by an infection can lead to hormonal fluctuations. Stress, whether physical or emotional, can impact the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that regulates hormones.
Hormonal imbalances, particularly involving estrogen and progesterone, can lead to irregularities in menstrual cycles. Women experiencing a UTI may find that their periods arrive later than expected or may be accompanied by additional symptoms such as increased cramping or mood swings.
Research indicates that stress on the body can alter menstrual patterns, and since a UTI can create significant physical stress, it is plausible that it may indirectly affect menstrual timing. Understanding this connection highlights the importance of treating UTIs promptly to minimize any potential impact on menstrual health.
How UTIs Can Impact Your Hormonal Balance
Hormonal balance is crucial for regular menstrual cycles, and any disruption can lead to irregularities. A UTI can affect hormonal levels due to the body’s immune response. When the body detects an infection, it releases inflammatory cytokines, which can lead to changes in hormonal regulation.
For instance, high levels of stress hormones like cortisol can alter the secretion of reproductive hormones such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones are pivotal in regulating the menstrual cycle. Disruption in their levels can lead to anovulation (failure to ovulate), causing delays in menstruation.
Additionally, the physical symptoms of a UTI, such as pain and discomfort, can contribute to stress and anxiety, further exacerbating hormonal imbalances. Chronic UTIs can lead to prolonged periods of physical stress, which may result in ongoing menstrual irregularities.
When to Consult a Doctor About UTI and Menstrual Changes
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if you suspect you have a UTI or if you experience changes in your menstrual cycle. Here are some guidelines on when to seek medical advice:
-
Symptoms of UTI: If you experience symptoms of a UTI, such as burning sensation during urination, frequent urge to urinate, or pelvic pain, seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment.
-
Menstrual Irregularities: If you notice significant changes in your menstrual cycle, such as a delayed period that persists beyond a week or changes in flow, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
-
Recurring UTIs: If you have frequent Utis (two or more within six months), it is crucial to discuss this with your healthcare provider to explore underlying causes and preventive strategies.
-
Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe abdominal pain, fever, or back pain, these could be signs of a more serious infection that requires immediate medical attention.
Understanding these signs can help ensure that both UTIs and menstrual irregularities are addressed promptly, leading to better health outcomes.
FAQ
Can a UTI cause a missed period?
While a UTI itself may not directly cause a missed period, the stress and hormonal changes associated with the infection can lead to menstrual irregularities.
How do I know if I have a UTI?
Common symptoms include a burning sensation during urination, frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain.
How are UTIs treated?
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics. It is essential to complete the full course prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Can stress affect my period?
Yes, physical stress from infections or emotional stress can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to changes in menstrual cycles.
When should I seek medical help for a UTI?
You should seek medical help if you experience symptoms of a UTI, notice changes in your menstrual cycle, or have recurring infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while a UTI may not directly delay your period, the stress and hormonal imbalances caused by the infection can lead to irregular menstrual cycles. Understanding the symptoms of a UTI and recognizing the potential impact on menstrual health is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. If you experience any concerning symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure your overall health and wellbeing are maintained.
References
- American Urological Association. (2020). Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of urinary tract infections
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2021). Urinary tract infection in adults
- World Health Organization. (2020). Hormonal contraceptives
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2020). Menstruation in girls and adolescents: Using the menstrual cycle as a vital sign
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Urinary tract infections